Company: Flipkart.com (a subsidiary of Walmart)
Founder: Sachin Bansal, Binny Bansal
Year founded: 2007
Headquarter: Bengaluru, India
CEO (Jan 2017 – Present):Kalyan Krishnamurthy
Number of Employees (2019): 30,000
Public or Private: Private
Industry Sector: E-commerce
Valuation (Nov 2020): $24.9 Billion
Annual Revenue (FY 2019): $6.1 Billion (Rs. 42,878 crore)
Products & Services: consumer electronics | ebooks | fashion | lifestyle products
Competitors: Amazon | Snapdeal | Alibaba.com | Paytm | Shopclues
Introduction to Flipkart, e-Commerce Platform
Flipkart e-Commerce Company was first idealized by Sachin and Binny Bansal in 2007. Both brothers are former Amazon executives. The Bansal brothers were able to successfully design a business module based on their experience and expertise. Their business scheme stood promising that led to the initial funding process from external sources.
Initially, the Bansal brothers invested in a total of $5,600 towards developing an ideal online book store website. 2 years after the initial launch, Flipkart platform stood potential enough to raise $1M from Accel India. They later formed alliances with Tiger Global, raising in a total of $10M in 2010 and $20M in 2011.
Flipkart had also reported that they have completed the 4thround of funding phase from MIH, a subdivision of Naspers Group and ICONIQ Capital. These funding were harvested for the very reasoning to further explore new business opportunities and venture to new business endeavors that would further improve and grow Flipkart as a company.
In July 2020, Walmart led another startup investment round for $1.2 billion, which raised Flipkart’s valuation to $24.9 billion. The US retailer owns over 90% of Flipkart for $16 bn; it invested in 2018. In September 2020, Walmart invested $560 million in Flipkart as part of the $1.2 billion investment round. [1]
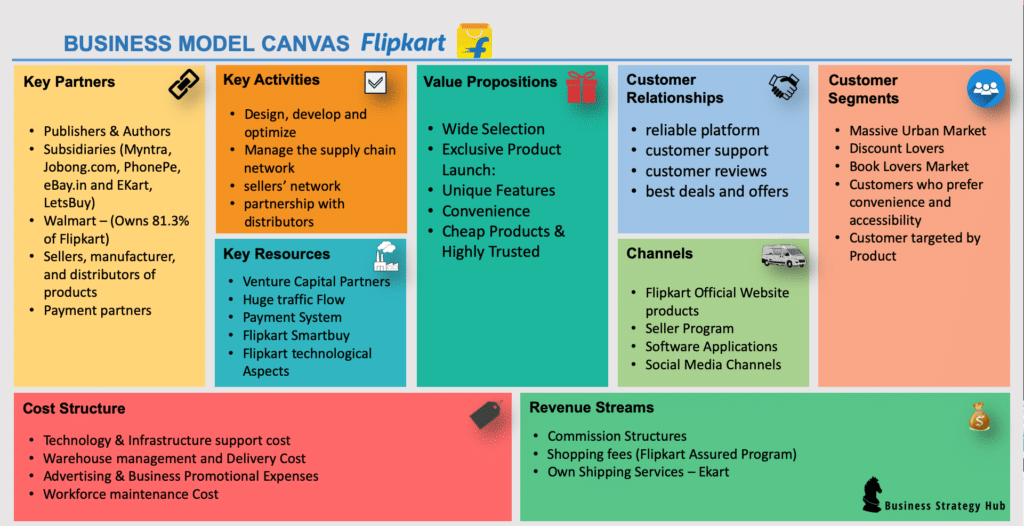
Business Model Canvas of Flipkart
Now let’s look at the business model canvas of Flipkart in more detail:
1. Flipkart’s Customer Segments
Massive Urban Market – who prefers to buy online
-
- Flipkart has grown into an enormous platform for a vast marketplace in India for the time being.
- Currently, Flipkart marketplace is only open and available for deliveries to be made anywhere within India.
Discount Lovers – Promotional Offers & Special Pricing for Customers
-
- Flipkart offers its loyal and new customer(s) promotional offers & special pricing during the holidays.
- They also provide branded products at reasonable prices – This is also a great way to ensure diligent treatment towards loyal customers and help further introduce its products to potential marketplaces.
Book Lovers Market Trend Analysis
-
- Flipkart originally started selling books and now have expanded to major electronics at a massive scale for adults and children.
Customers who prefer convenience and accessibility
-
- Flipkart products are easily accessible through their official website.
- Flipkart products can be accessed through Flipkart’s software applications programs. (Google Play & iTunes)
Customer targeted by Product
-
- Flipkart’s most success is driven by the smart analytics that is evaluated for the market places.
- Its social media platforms are another set of sources that help the analyst identify what consumers are into nowadays, and what is the recent trend.
- Flipkart targets those products that are in high demand to potentially make a sale.
Online Retailers
-
- Some online retailers don’t have extensive delivery systems and rely on Flipkart via Ekart logistics and shipping services. [2]
2. Flipkart’s Value Propositions
Exclusive Product Launch:
-
- Electronics
- TVs & Appliances
- Baby & Kids
- Home & Furniture
- Sports, Books & More
Unique Features
-
- Customer Login & Signup area
- Sell on Flipkart as a Seller
- 24x 7 Customer Services
- Advertise with Flipkart
- Software Application (Dual Interface)
- Flipkart Assured– badge for high-quality products and faster delivery.
Convenience
-
- Before the Flipkart launch, India consumers used to purchase such goods directly from Amazon, Ali Baba, Snapdeal and other competitive platforms that offer almost the same types of products and services.
- When Flipkart launched with competitive products with low prices, the Indian consumers’ interest rose in the local Indian Amazon, i.e., Flipkart.
- In 2020, it launched Flipkart Wholesale to provide services for the grocery and fashion categories. The expansion is focused on enhancing India’s wholesale ecosystem. To deliver this project, the company acquired Walmart India that operates Best Price, and also plans to provide technical support to Kiranas and MSMEs since they play an integral role in the sector. [3]
Wide Selection
-
- Users are able to find just about any type of product, whether it is for the holidays, searching for a gift or just doing some general shopping.
- Flipkart Users are able to search through thousands of different sellers and review the listings that they have.
- Each listing (product) is listed with product specifications and details. Users are able to search through category or through smart search (filter engines)
Cheap Products & Highly Trusted
-
- One of the best things about Flipkart is that fact that they offer their clients to review the listing from these sellers and other relevant shops that offer their products at the lowest prices as compared to the markets.
- Because of their policies, due diligence, and the positive feedback, Flipkart is highly trusted and recommended by customers who have used the Flipkart services before.
- Trust credibility factors help to increase business potential revenue streams by reference or through retention conversions.
3. Flipkart’s Customer Relationships
Flipkart aims to establish a global recognition as one of the leading e-commerce platforms. Since the initial launch in 2007, Flipkart has built a sound relationship for their loyal customers and followers.
-
- Flipkart ensures to provide its customers with the best deals and offers that are more beneficial as compared to other competitive companies.
- Flipkart has created a reliable platform that provides quality products with customer reviews.
- Flipkart ensures to provide quality customer support via phone, online chat or email available 24-7.
4. Flipkart’s Key Activities
The following are the major key activities that are conducted daily that help to deploy all the operations of Flipkart
-
- Design, develop and optimize its ingenious online platform specifically for electronic commerce products for the Indian Regions.
- Manage the supply chain network of its products including logistics, warehouses, etc.
- Hire, train and retain the workforce.
- Product catalog– maintain product catalog with images and videos.
- Build and manage sellers’ network.
- Establish a partnership with distributors and other manufacturers.
- Marketing & Sales promotion including developing an effective Pricing strategy and promotional offers and discounts during shopping peak seasons and holidays.
- Establish a secure payment portal.
- Customer support (24 – 7) via phone, online chat, and email.
- Acquisitions for expansion- To expand into the wholesale sector, Flipkart acquired a 100% stake in Walmart’s India business. This enabled the online retailer to launch Flipkart Wholesale to serve small and medium-sized businesses and neighborhood stores (Kiranas) in India. [4]
5. Flipkart’s Channels
One of the most significant reasons for Flipkart success is the powerful combination of Flipkart revenue model and other digital marketing schemes that spread like wildfire across the internet, creating its online presence, awareness and helping to further channel Flipkart for opportunities.
Website
-
- Flipkart Official Website products
- Seller Program
- Affiliation Programs (promotional content)
- Flipkart Plus
The website alone provides additional features, promotional deals and other exclusives that helps it landing pages convert.
Software Applications
Additional accessible platforms like Flipkart software applications help potential customers to process other potential orders.
Social Media Channels
Through the social media channels, Flipkart is able to publish blogs, news and other promotional material that helps to increase the awareness of Flipkart. Thus, increasing new revenue streams.
6. Flipkart’s Key Partners
In association with the branding phase, Flipkart was built with the assistance of its primary key partners. Each associated member has relevant experience and knowledge in their respective professional field, and took part to make company business models, and other endeavors to motion:
Publishers & Authors
-
- Flipkart was originally launched as a book buying platform, offering a wide selection of book and eBook for readers to select and purchase.
- The company soon flourished and expanded its line of products, converting the business model to the wider side of the spectrum.
Subsidiaries (Myntra, Jobong.com, PhonePe, eBay.in and EKart, LetsBuy)
-
- Flipkart’s subsidiaries provide a wide range of products to generate additional revenue with higher profit margins. Some of the new subsidiaries include Mallers, DSYN, Ugenie, Jeeves Consumer Services, and AdiQuity.
- Most of these subsidiaries were launched prior to achieving the financial goals through their financial investors and capital start-up grants.
Walmart – (Owns 81.3% of Flipkart)
-
- Walmart is an American multinational retail company that operates in multiple sectors.
- Headquartered in Bentonville, Arkansas. On May 2018, Walmart acquired 81.3% of Flipkart. In 2020, Walmart increased its stake in Flipkart by leading a new $1.2 billion financing round to add on top of the $16 billion it invested in the Indian e-commerce giant two years ago. [5]
Sellers, manufacturer, and distributors of products
Flipkart massive inventory system is supplied by some of the prime titans in India:
-
- Sellers – Sellers that sell their products or services via Flipkart through means of operating a “store-presence” on the Flipkart platform.
- Flipkart is responsible for delivering the goods. However, the supply chain (products or services) are directed by the supplier/sellers’ end.
- The sellers are responsible for fulfilling the orders that they Sellers claim to sell/promote.
Payment partners
Flipkart has partnered with Banks, Credit card, e-wallet companies to offer secure payment service on its platform. In 2020, it partnered with Paytm to meet the increase in demand during the festive season. The partnership also provided customers a wide variety of offers and benefits under The Big Billion Days festive season sale. [6]
7. Flipkart’s Key Resources
Initial resources that makeup Flipkart, consists of a group of multiple investors that help fund the structure of Flipkart operations and for further development.
Resources (2007- Present):
Flipkart venture capital funds partners;
-
- Accel India
- Tiger Global
- MIH (Naspers Group Sector)
- ICONIQ Capital
- Japan’s SoftBank
- In preparation to take on Flipkart’s biggest competition– Amazon. In 2017, Flipkart had $2.5B from Japan’s SoftBank. In 2018, however, SoftBank had sold all (20% stake in Flipkart) of its share to Walmart.
Huge Traffic Flow
-
- One of the most crucial factors for Flipkart is that fact that its ability to get over 100 million visitors every day. To reduce delays, Flipkart launched a hyperlocal delivery service in July 2020 known as Flipkart Quick, which provides a handpicked assortment of over 2,000 products in categories and delivers to the customer within 90 minutes. Some of the most common products for Flipkart Quick includes grocery, meat, dairy, and other essentials. [7]
- The conversion rate + recurring loyal customers and the conversion rate from reference or third-person help to generate revenues for the company.
- Flipkart not only do customer come back to shop again through Flipkart channels but also help to create awareness of the company and increase company image.
Payment System
Flipkart platform offers multiple methods for its customers to pay for their orders:
-
- COD (Cash on Delivery) – The concept that was pioneered by Flipkart has changed the game of e-commerce in Indian Market. A customer that would like to place an order on COD can place orders that do not exceed 50,000 Indian Rupees (Approx. $700). In 2020, Flipkart rolled out partial payments that allow customers to pay part of the total price of a product when they order it and settle the remainder on delivery. The unpaid part of the price is collected via the Cash on Delivery (CoD) system. [8]
- Credit / Debit Card – During the sign-up phase, clients are required to provide either a credit card or debit card. Such cards can be issued from India or the other 21 countries that Flipkart accepts to do business with.
- Bank’s Internet Banking feature – Customers have the option to sync their Flipkart accounts with their local banking facility to process payments.
Flipkart SmartBuy
-
- Flipkart’s private labelSmartBuy is created to introduce its loyal customers a channel to supply mobile & electronics accessories, home & kitchen appliances at affordable prices.
Flipkart Technological Aspects
-
- Flipkart’s technology and infrastructure have enabled them to deliver 5 million products per month.
Sachin Bansal– Executive Chairman
-
- Sachin Bansal (former Amazon Executive) is currently the owner of Flipkart.
- S. Bansal is currently looking into new business opportunities and possibly is interested in making investments to new merging markets and continue to explore different industries further.
- S. Bansal owns about 6% of Flipkart, Inc. shares.
Binny Bansal– Co-founder & CEO (Helping Founders)
-
- Binny Bansal (former Amazon Executive) is also the owner of Flipkart.
- Binny Bansal is no longer working with Flipkart due to an allegation raised by 81.3% shareholder Walmart. Currently, there hasn’t been any recent releases regarding the allegations.
- B. Bansal was believed to be 5% owner of Flipkart shares.
Kalyan Krishnamurthy– CEO
-
- Kalyan Krishnamurthy is currently the CEO of Flipkart. Mr. Krishnamurthy mentioned that Flipkart will soon be required to hire additional executives for the company.
- Krishnamurthy is responsible for all the operations that are deployed regularly in the Indian region.
- Flipkart is still considered a domestic company, and Walmart has unveiled plans about continuously keeping Flipkart accessible in its home country – India.
8. Flipkart’s Cost Structure
-
- Technology & Infrastructure support cost
- Warehouse management and Delivery Cost
- Advertising & Business Promotional Expenses– went up by 9.4% to Rs. 1,188 crores in 2017, as compared with a 100% jump in 2016. Flipkart increased its ad expenses by 56% from Rs 731.3 crores in FY2018 to Rs 1141 crores in FY2019. The increase is attributed to stiffening competition, which requires Flipkart to pay for more digital ads across several platforms to attract and retain customers. [9]
- Workforce maintenance Cost
- Employee Cost Monthly: The average salary per employee is approx. $981.73 per monthly basis cycle (approx. 70,000 Indian Rupees)
- Employee Cost Annually: There are in total of 30,000 employees x $981.73 average salary = $30 Million
9. Flipkart’s Revenue Streams
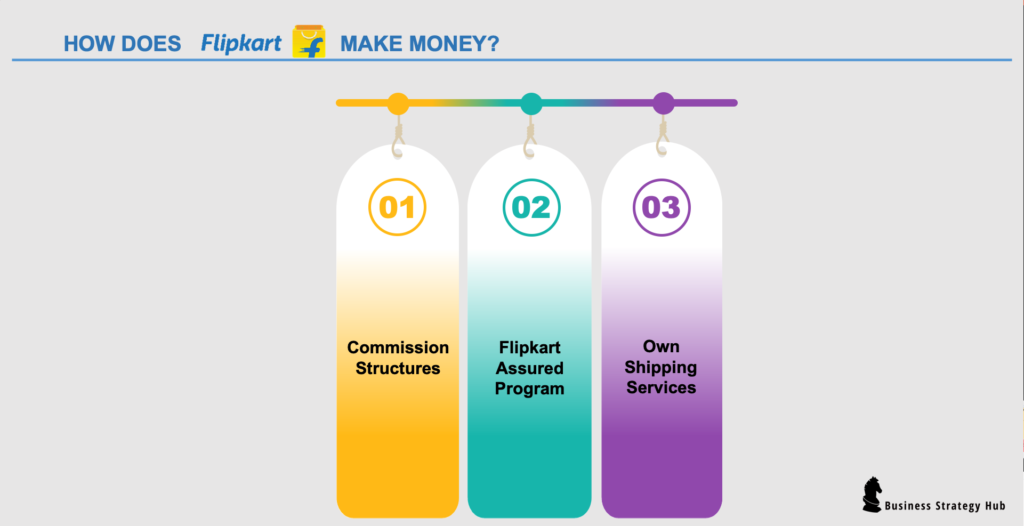
Flipkart accumulates its revenue through a few channels. Let’s see how does Flipkart make money?
How does Flipkart make money?
Commission Structures
-
- Flipkart makes a percentage cut whenever someone sells their product to a customer. Commissions are usually deducted from the original transaction value prior to paying out the seller who sold the item.
The commission structures vary from item to item, they are categorized in the following;
-
- Low Margin branded categories: 2-5%
- High Margin branded categories: 10-25%
Shopping fees (Flipkart Assured Program)
-
- Shopper saves more by availing free deliveries on orders that exceed the value of 500 Indian rupees. The saved amounts usually are accumulated and then spent again at Flipkart.
Own Shipping Services – Ekart
-
- It is a department that makes all the deliveries of goods to the concerned consumer.
- It costs 50 Indian Rupees for items that are less than half a KG (weight)
- Flipkart also makes money using Ekart to ship products of other retailers who have customers in India but lack logistical capabilities.
Paid Ads
-
- The e-commerce giant has been generating a lot of money from paid ads since. It launched a digital ads platform in 2015, which attracted businesses quickly and was generating nearly $1 million in monthly advertisement sales within a year. Flipkart is regarded as one of the largest digital ads platforms in India. [10]
Final Thoughts
The success of Flipkart may not be very much dependent on the fact that it operates similarly to Amazon, instead because of the market trend and scope in India.
Although there are Amazon facilities designated in India, Flipkart online platform offered similar brands and products, only this time Flipkart doesn’t charge additional international shipping charges and therefore delivery is much cheaper as compared to what Amazon charges. Because of the demand and scope in India existed, the success of Flipkart was made possible.
References & more information
- ET Tech. (2020, Sep 26). Walmart invests $560 million in Flipkart. Economic Times.
- Editor (2020, Sep 29). 700 Kirana stores to assist Flipkart’s Ekart in last-mile delivery. Indian Online Sellers
- Danny Cyril, D. (2020, July 23). Flipkart Wholesale to be launched next month: 5 things to know. Live Mint
- Singh, M. (2020, July 23). Flipkart buys Walmart’s India wholesale business to reach mom and pop stores. Tech Crunch
- Singh, M. (2020, July 14). Walmart leads a $1.2 billion investment in India’s Flipkart. Tech Crunch
- PTI. (2020, Oct 5).Flipkart partners Paytm for festive sale. Economic Times
- Bapna, A. (2020, Sep 30). Brand bounce-back: Flipkart marketing lead expects the Indian festive season to trigger growth. The Drum
- Verma, S. (2020, July 17). Flipkart rolls out partial payments to reduce order cancellations. India Today
- Mansuri, M. (2020, Jan 7). Flipkart Internet upped ad spends by 56% in FY19. Exchange 4 Media
- Editor. (2020, Sep 9). Flipkart clocks $1mn monthly revenue from paid ads; Launches ‘Brand story ads.’ Indian Online Seller
Tell us what you think? Did you find this article interesting? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below.











Really its very good for me helping me to Growing my future company
Glad you liked the article JP.
I wish you all the success for your company !