Company: Tata Motors Limited
Founder: Jamsetji Ratanji Dadabhoy Tata
Year founded: 1945
Executive Director: Girish Wagh
Headquarter: Mumbai
Employees: 81,811
Type: Public
Ticker Symbol: TTM
Annual Revenue (FY24): Rs. 4,37,928 Crores
Profit | Net income (FY24):–Rs. 62,800 Crores
Products & Services: Passenger Vehicles (Cars & UVs) | Commercial Vehicles (Trucks & Buses) | Jaguar Land Rover | Motor Vehicle Financing | Eclairs | Oreo | Bournvita
Competitors: Maruti Suzuki | Hyundai | Honda | Ford | Toyota | BMW | Mercedes | Volkswagen | Tesla
Fun Fact:
- Tata Motors built the first Indian Indigenous car, Tata Indica, in 1998 and first sports car
- Tata Motors owns Jaguar Land Rover
- Tata Motors is the backbone of the Indian Army Vehicles
- Tata Motors built the world’s costliest version of its cheapest car that cost $1,200
Tata Motors Overview
Founded in 1945, Tata Motors is a key player in the global automotive industry with a diversified product portfolio. A subsidiary of Tata Group, it designs, manufactures, and sells various cars, including fossil fuel and electric vehicles.
Operating in over 120 countries, it also focuses on engineering and tech-enabled automotive solutions. The company is pioneering India’s electric vehicle revolution and enjoys an advantage in one of the fastest-growing automotive markets.
Tata Motors Strengths
1. India’s third-largest carmaker
Tata controlled 14.85% market share in India’s automotive sector as of the end of 2023 year overtaking Hyundai that came in third with a 13.79% market share.
2. Broad market reach
Tata Motors is in over 125 countries, with a worldwide network of over 8,800 touchpoints.
3. Focus on innovation
Tata Motors invests heavily in innovation to enhance its vehicles’ performance and make them competitive in the market. For starters, it has invested in advanced driver assistance systems as it seeks to build self-driving cars.
Its investment in connected car technologies demonstrates its dedication to innovation as it looks to unlock new opportunities, reach new markets, and safeguard its future in the highly competitive auto industry.
4. Brand Reputation
Tata Motors enjoys a solid reputation for developing quality and reliable automobiles. This strong brand recognition has allowed it to attract a loyal customer base and maintain its position as one of the largest automakers.
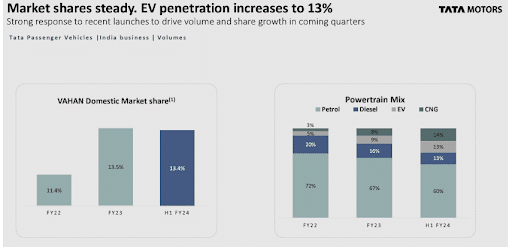
Image Source: Tata Motors
Since 2021, it has consolidated sales while establishing itself as India’s best-performing EV car manufacturer, powered by sales from its flagship Nexon EV and the Tigor EV.In 2023, it achieved a significant milestone on selling 50,000 electric cars accounting for 9.2% of its total vehicle sales of about 5.41 Lakh units.
5. Production of future-ready vehicles
Tata launched an all-new range of BS6-compliant vehicles across its CV segment in FY21. It is launching eight upcoming Tata cars, Altroz Racer, Curvv EV, Curvv, Avinya, and Harrier EV, which will be launched in India in 2024-2026. Among these eight upcoming cars, there are 2 Hatchbacks and 11 SUVs.
Tata is also pioneering the production of electric and hybrid buses. The automotive maker also launched CNG-powered vehicles for its green segment in January 2022.
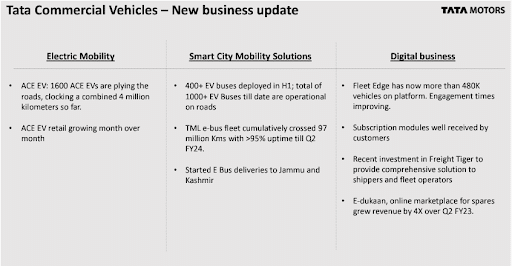
Image Source: Tata Motors
6. Broad revenue stream
Tata Motors is not only a car manufacturer but also a service provider. In addition to generating revenue from selling cars, the company also makes money by offering financial services through its Tata Motors Finance subsidiary.
Some of the services provided include insurance services and extended warranties. The diverse product range has helped build customer loyalty to the brand
7. Diversified products and services
Tata Motors provides a variety of vehicles to meet the needs and preferences of different types of customers. Its product line includes passenger cars, SUVs, commercial vehicles, buses, and electric vehicles. Its commercial vehicle (CV) segment’s growth is ahead of its competitors, with a 39% market share in the commercial vehicle (CV) segment.
Tata Motors Group has four primary product segments:
- Jaguar Land Rover (JLR) – represents 69.12% of the total revenue.
- Commercial Vehicles (CV) – represents 17.98% of the revenue.
- Passenger Vehicles (PV) – represents 11.95% of the revenue
- Vehicle Financing and Others – represents 0.93% of the revenue.
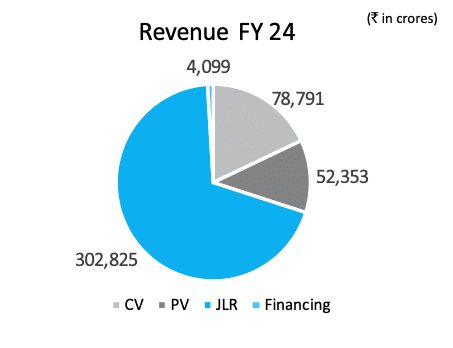
Image source: Tata Motors annual report
- Clever market segmentation of its vehicles – Tata models have a price ranging between Rs 5 lakh to Rs 20 lakh, meaning there’s a car for almost every customer. Tata vehicles have 10 to 14 variants, which gives the buyer something to choose from at every Rs 20,000 mark.
- Through its subsidiary, Tata AIG, the manufacturer not only offers insurance cover for its motor vehicles but also provides repair services that form a vital component of its after-sales services.
- Other products in its portfolio include fleet management solutions, annual maintenance packages, Tata Alert roadside assistance service, and resale for commercial vehicles.
8. Global Presence
Tata Motors is a global company with a strong presence from Europe to Africa, the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and South America. The worldwide presence has allowed the company to unlock new opportunities in niche markets and therefore diversify its revenue base. Below is the geographical breakdown of its revenue.
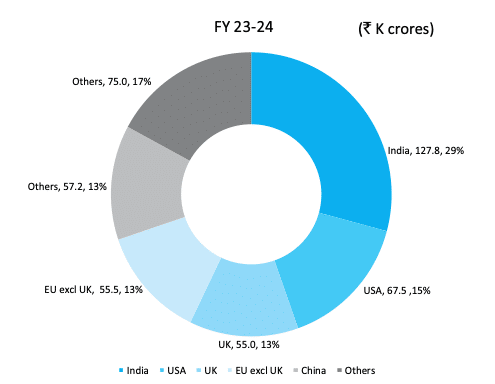
Image source: Tata Motors annual report
9. Strong focus on quality and safety
Tata has shifted its focus towards first-rate quality in product development and manufacturing systems, bringing on board global suppliers to improve car makers’ quality standards. In 2018, Tata Nexon was the first made-in-India, sold-in-India car to get a five-star crash test rating from Global NCAP. Altroz, its other model, also achieved a five-star rating in 2020.
10. Strong performance by Jaguar Land Rover (JLR) acquisition
Acquiring Jaguar Land Rover (JLR) in 2008 gave Tata Motors access to premium vehicle segments, innovative technology, and a global presence. This has enabled the company to broaden its product portfolio and strengthen its competitive edge in the luxury car market.
Jaguar Land Rover represents 69% of total Tata motors consolidated revenue.

Image source: Tata Motors annual report
Tata Motors Weaknesses
1. Reliance on Indian Market
Tata Motors has achieved considerable growth in its global operations but continues to depend largely on the Indian market for income generation. This dependence on the Indian market poses a risk, particularly amid economic instability, which might lead to a reduction in car purchases by consumers.
The Indian automotive sector is intensely competitive, featuring many well-established companies. As a result, shifts in market conditions, shifts in consumer preferences, or changes in regulatory frameworks could greatly affect Tata Motors’ success.
2. Dependence on the Jaguar and Land Rover Segment
Tata Motors’ business model heavily depends on the Jaguar and Land Rover segment that generated Rs 302,825 crore compared to the second-placed Commercial Vehicle at Rs 78,791 and third-placed Passenger Vehicle segment at Rs 52,353.
While this segment is profitable, it exposes the company to the cyclical industry. From economic downturns to changes in freight demand and regulatory changes, this segment significantly impacts the company’s overall performance.
3. High Debt Levels
Tata Motors’ debt-to-GDP ratio is very high, which can be a significant handicap for the company. As of September last year, the automaker had about $15.39 billion in debt on its balance sheet.
A high level of debt can lead to an increase in interest expenses, hurting the company’s bottom line. Furthermore, it can restrict the company’s ability to fund new initiatives or technologies.
4. Quality service concerns
Tata Motors has received a lot of flak in the past for the low quality of some of their vehicles and the poor after-sale service provided by their dealer network.
Although the company has taken steps to address these issues, any perception of poor quality or poor service can damage the company’s brand image and customer loyalty.
5. Limited Luxury car market exposure
While the acquisition of Jaguar Land Rover has opened the door for Tata Motors to enter the luxury vehicle segment, its presence in this segment still needs to be improved compared to many of its global rivals. Consequently, Tata Motors may need to catch up on growth prospects in the luxury segment, which typically has higher profit margins.
Tata Motors Opportunities
1. CNG powered vehicles
Tata Motors is staring at a massive opportunity amid growing demand for compressed natural gas vehicles. India’s CNG Market is valued at about $9.37 billion and is expected to reach $13.95 billion by 2030 while growing at a compound annual growth rate of 6.87%.
Tata Motors has a huge opportunity in the CNG-powered vehicles.
2. Hydrogen fuel cell technology
Tata Motors is also staring at a massive opportunity as the hydrogen fuel market grows at 43% and is expected to be worth $57.9 billion by 2032.
Government incentives are expected to reduce running costs for these vehicles, making them more attractive as a mass transport option. There is optimism that demand for this technology will surge towards the second half of this decade.
3. Electric vehicles
The global electric vehicle market is growing at a CAGR of 13.7% and is expected to be worth $951.9 billion by 2030. India’s EV market is growing at a CAGR of 66.52% and is expected to be worth $113.9 billion.
The rate of electric vehicle adoption in India has surpassed most predictions, especially for electric two- and three-wheelers. Tata Motors has registered a staggering 353% percent volume growth in the electric vehicle segment, and there is still room for further development.
4. Domestic market growth
A report by Goldman Sachs’ BRIC Team predicts a significant rise in the middle-class population in India. Its middle-class population of over 350 million is larger than the entire US population and matches that of the EU.
With an improvement in per-capita GDP and purchasing power parity, Goldman Sachs expects India to hit the “sweet spot of car ownership” presenting a massive market opportunity for Tata Motors with its array of cars.
5. Improved business environment
Demand for Medium & Heavy Commercial Vehicle (M&HCVs) has improved during the post-lockdown phase owing to India’s economic recovery and the Government’s increased focus on the construction and mining industry.
Specifically, the Gati Shakti scheme, which includes mega infrastructure projects, is expected to favor construction and allied sectors, thereby spurring growth in the M&HCV segment. The expansion of the national highway network by 25,000 km, envisaged in FY23, is expected to drive demand for cement and steel and boost the heavy commercial segment.
6. Expand its luxury segment
India’s luxury car market presents tremendous opportunities as it was valued at $1.08 billion in 2024. The fact that it is growing at a CAGR of 5.4% and expected to be worth $1.64 billion by 2031 presents a massive market that Tata Motors can tap into.
Tata Motors can tap into the massive opportunity in the luxury car market. Luxury car sales increased by 20% in 2023 to record highs of 42,731 units.
7. Emerging markets opportunity
Tata can also unlock growth opportunities in Africa, where the automotive market is valued at USD 20.5 billion and enjoys a significant presence in South Africa, Angola, Kenya, Morocco, Nigeria, and Ghana, to name a few.
Tata Motors’ expansion into new, untapped markets, both at home and abroad, presents a massive opportunity for the company to expand its customer base and revenue. For instance, Tata Motors could target markets where it doesn’t have a presence, such as in some countries in Latin America, Africa, or Southeast Asia.
Tata Motors Threats
1. Strong market competition
Tata Motors is up against tough competition from both local and international car manufacturers, such as Hyundai and Toyota. These competitors, which span from new companies to well-known brands, offer products that are either identical or superior at affordable prices.
In this intensely competitive environment, Tata Motors must continuously innovate and update its business strategy to maintain its lead and attract customers.
2. Cybersecurity threats
Like any global organization, Tata Motors is vulnerable to cybersecurity threats in the digital transformation era. The company holds large volumes of customer and operational data, making it an ideal target for cybercriminals.
Cyberattacks on Tata Motors could compromise sensitive customer information and operational secrets, resulting in a loss of customer confidence and revenue and potential legal issues. As a result, Tata Motors needs to invest in a robust security infrastructure and constantly track and update its systems to stay ahead of ever-changing cyber threats.
In June 2021, The Business Standard reported that cybersecurity researchers in India had discovered a malicious gift campaign disguised as an offer from Tata Motors. The malware was used to collect users’ data and is believed to have been carried out by China-based hackers.
3. Supply chain issues
- The negative impact of the semiconductor shortage has constrained Jaguar Land Rover retail sales in FY22.
- Lithium-ion battery availability, critical to Tata’s EV production, also poses supply chain risks to the automaker.
- In addition, Supply chain disruptions occasioned by China’s lockdowns and dealership closures have affected Tata car sales, leading to negative EBIT and free cash flows in the 2022 fiscal year.
4. Economic Downturn
An economic downturn can significantly impact consumer spending, leading to a decrease in sales and profitability of Tata Motors. Consumers tend to put off big purchases like cars when the economy is uncertain, which could hurt the company’s sales.
In addition, an economic recession can also lead to an increase in competition as companies try to keep their market share. This can lead to a further decrease in Tata Motors’ profitability.
5. Regulatory issues
Like any other global company, Tata Motors is vulnerable to regulatory threats. The company operates in different markets worldwide, where regulations and compliance requirements vary from country to country.
Regulation changes, such as emission or safety standards, can significantly impact Tata Motors’ business and necessitate significant investments in product and process innovation. Failure to adhere to regulations can lead to penalties, hurting a company’s bottom line and brand image.
6. Raw Materials fluctuating prices
The car manufacturing sector relies heavily on basic materials such as steel, aluminum, and rubber. Changes in the cost of these materials can significantly affect Tata Motors’ production expenses and, consequently, its earnings. While some of these price hikes can be transferred to the buyers, the competitive environment and market circumstances frequently stop the company from doing so, adversely affecting its profit margins.
References & more information
- Patel, D. (2023 June 28). Tata Motors’ permanent employee strength rises after three years: Report. Business Standard.
- Rajan, S. (2024 March 30). Despite disappointing year, Tata Motors aims to more-than-double EV sales in 2 years. The New Indian Express.
- Sun, S. (2023 September 20). Market share of commercial vehicles across India in financial year 2021 and 2023, by manufacturer. Statista.
- One, A. (2023 August 16). The business engine of Tata Motors: Exploring the company’s revenue streams. Angel One.
- (2024). India CNG Vehicles Market SIZE & SHARE ANALYSIS – GROWTH TRENDS & FORECASTS UP TO 2030. Mordor Intelligence.
- (2023 October). Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle Market Size, Share, Competitive Landscape and Trend Analysis Report. Allied Market Research.
- (2023 October 25). India’s Booming Electric Vehicle Industry. Confederation of Indian Industry.
- Syed, A. (2022 March 9). Tata Motors: Leading change with innovation. Manufacturing Today.
- (2024). India Luxury Car Market Valuation – 2024-2031. Verified Market Research.
- Philip, L. (2024 January 15). Luxury car sales in India surge to record high, up 20% YoY. The Economic Times.
- (2021 June 10). China-based hackers luring Indians into fake malicious Tata Motors scam. Business Standard.
- Abbott, A. (2022 November 14). Top 15 Intel Competitors & Alternatives. Business Strategy Hub.
- (2022 April 9). Tata Motors owned-Jaguar Land Rover Q4 FY22 retail sales drops 36% YoY. Business Standard.
Tell us what you think? Did you find this article interesting? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below.












Kevin Johnson presents a solid SWOT analysis! Tata Motors’ innovation in EVs and ADAS tech is truly shaping the future. Their strong market presence and global reach make them a force to watch in the auto industry!