Company: Wells Fargo & Co.
CEO: Charles W. Scharf
Founders: Henry Wells, William Fargo
Year founded: March 18, 1852
Headquarters: San Francisco, California, United States
Employees (FY2023): 225,870
Ticker Symbol: NYSE: WFC
Type: Public
Annual Revenue (FY2023): $82.59 Billion
Profit | Net income (FY2023): $17.98 Billion
Products & Services: Banking | Online Banking | Loans | Credit Facilities | Merchant Services | Insurance | Payroll | Investments | Retirement Plans | Wealth Management | Rewards and Benefits.
Competitors: JPMorgan Chase | Bank of America | Citibank | Goldman Sachs | Morgan Stanley | U.S. Bank | HSBC | UBS
Fun Fact:
Wells Fargo was the first bank to introduce online banking way back in 1995. It also rolled out online money-management services by 2005, making it one of the first.
The company has a Wells Fargo Museum in San Francisco. Displays include original stagecoaches, photographs, gold nuggets and other artifacts.
Wells Fargo is one of the best-known financial institutions globally. It operates in community banking, retail banking, commercial banking, wholesale banking, investment management, corporate banking, online services, and many more.
While it is one of the ‘Big Four’ banks in the US, the company does business in many parts of the world. It has more than 70 million customers in 35 different countries.
With over 170 years under its belt, and having moved from stagecoaches to high tech, we can learn plenty from Wells Fargo. Here is an in-depth SWOT analysis of Wells Fargo.
Wells Fargo’s Strengths
With extensive global operations and a strong brand, Wells Fargo is a force to be reckoned with in the banking sector. Below are the company’s strong points.
1. Global Presence
Operating globally is a major strength since it gives the company access to a deeper pool of potential banking customers.
Wells Fargo operates in many parts of the world from North America to Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Middle East. It has international offices in many large cities, including Paris, London, Dubai, Tokyo, Shanghai, and Beijing. These offices provide commercial banking services and not consumer banking.
2. Strong Brand Recognition
Wells Fargo serves one out of three U.S households and over 10% of small businesses in its domestic U.S market. It shows Wells Fargo has a loyal customer base and strong brand recognition.
3. Strong Financials
Having immense financial resources allows companies to acquire all they need to compete more effectively. Post-pandemic, Wells Fargo has been strengthening its financial position. After a sudden decline in 2020, Wells Fargo has bounced back and has substantially increased its profitability (net income) from $3.3 billion in FY2020 to $19.1 Billion in FY2023.
4. Part of the US Big Four
The US banking sector is dominated by four large financial institutions. They are:
- JPMorgan Chase & Co
- Bank of America
- Citigroup, and
Wells FargoMembers of the big four influence policymaking immensely.
5. Top 20 in the World
Wells Fargo is listed among the largest banks in the world, measured by total assets. It is at #16 on the list with assets of $1.9 billion.
6. Leader in the Middle Market Segment
Wells Fargo has the #1 banking share in middle market companies (with $25 to $500 million in annual sales) in the United States. Small and medium-sized enterprises are important economic drivers. Wells Fargo has captured this segment and enjoys all the benefits of vast financial resources that flow in and out of the US middle market segment.
7. List of America’s Largest Corporations
Since its founding, Wells Fargo has focused on working for small and medium businesses. This has enabled the company to build a highly valuable brand, and it is ranked # 47 on Fortune’s 2023America’s Largest Corporations list.
8. Highly Valuable Global Banking Brand
In the Brand Finance 2024 report, Wells Fargo was ranked #6 most valuable global banking brand with a brand value of $35.8 billion, up from the #8 spot the year before.
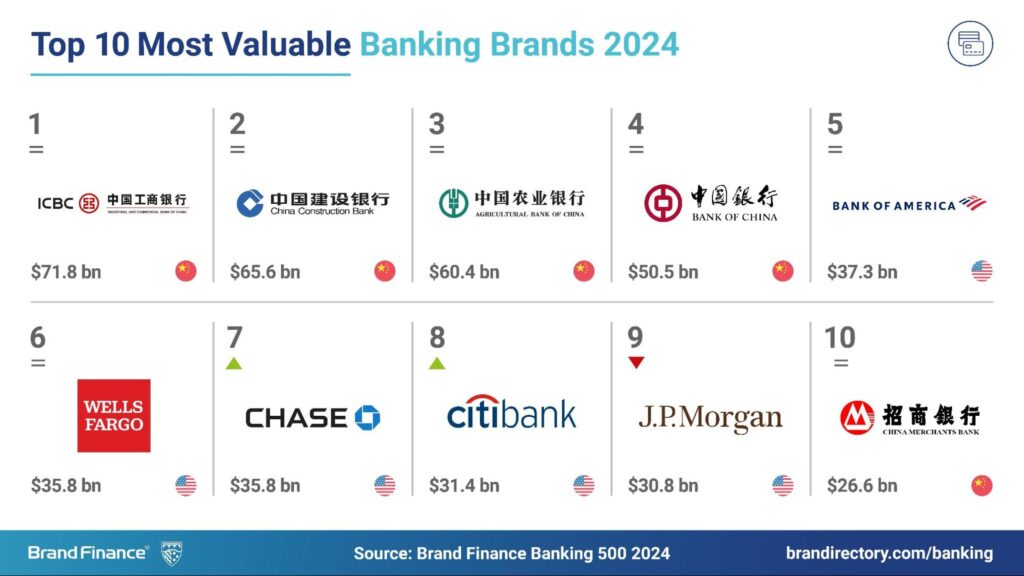
Source: Brand Finance
9. Exemplary Performance
Wells Fargo is one of the high-performing banks and was given an “outstanding” rating for community lending from the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency.
10. Variety of Service Offerings
Wells Fargo offers a wide variety of services that cater to the entire market. It offers banking and online banking services, loans, merchant services, investing, and so on, catering to the following segments:
- Consumer banking and lending – is the largest segment of Wells Fargo, representing about 46% of total revenue. It provides services such as loan lending to consumers and small businesses, home lending, credit card, and auto loans.
- Commercial Banking – represents about 16% of total revenue. It includes middle market banking and asset-based lending and leasing.
- Corporate and Investment banking – represents about 23% of total revenue. It provides banking services on mergers and acquisitions, IPO, commercial real estate, markets sales & trading, risk management, and financing services to corporations.
- Wealth and investment management – represents about 17% of total revenue. It provides asset management services through Wells Fargo Advisors and Wells Fargo Private Bank.
- Corporate and reconciliations – represents about -3% of total revenue. This is the central-function segment of the whole bank, including revenues from the corporate treasury, the group’s investment portfolio, affiliated venture capitals, private equities, and non-strategic businesses.
Wells Fargo’s Weaknesses
Wells Fargo has faced some scandals and negative publicity in recent years. These are among the company’s weaknesses.
1. Fake Accounts Scandal
Years after it happened, the fake accounts scandal continues to make news.
In 2016, it was revealed that Wells Fargo’s employees opened millions of fake accounts, using the names of customers without their consent, in order to meet sales quotas. Eventually, the bank agreed to pay a $3 billion fine as settlement.
In September 2023, a former Wells Fargo executive was sentenced to 3 years probation due to her role in the fake accounts scandal. She oversaw an aggressive sales strategy that resulted in the fake accounts.
After the incident, Wells Fargo made changes to management and the board of directors.
2. Missed Opportunities
The fake account scandal had big consequences for Wells Fargo. As punishment, the Federal Reserve capped the number of loans Wells Fargo could give out. The bank reached this cap quickly during the distribution of the Small Business Paycheck Protection Program (PPP), with most of its small business clients missing out on aid valued in the billions.
The cap on loans was part of a larger punishment capping the bank’s assets. That cap remains in place, although PPP loans are no longer included.
3. Aging Systems
For years, Wells Fargo has ben working on updating its antiquated banking systems, The old systems make it harder for the bank to satisfy regulators and customers. The old systems break down more often and are harder and less intuitive to use, hampering key operations and inconveniencing their customers.
While the company is working to upgrade systems, work remains to be done.
4. Negative Publicity Incidents
Even the most loyal customers can decide to move to competitors if their bank faces accusations and investigations. Loyalty was tested after the fake accounts scandal, and an investigation surrounding distribution of PPP aid. Wells Fargo has work to do in order to regain their trust, or risk losing their customers to competitors.
5. High Operational Costs
With billions of dollars lost either due to aging machines or being paid as settlements, Wells Fargo’s self-inflicted wounds have resulted in increased operating costs. This undermines profitability and long-term sustainability.
Wells Fargo’s Opportunities
Wells Fargo has some opportunities to expand, diversify, and modernize. Here is a list of opportunities for the company.
1. Increasing Share of Investment Banking Business
The investment banking business represents a billion-dollar opportunity to expand market share.
With global investment banking revenue expected to be $0.38 trillion US in 2024, there is plenty of money to be earned in the investment banking sector. The longer-term outlook of this indudustry, from 2024 to 2029, is projected to reach 0.42 trillion US – a CAGR of 2.2%. Historically, the bank has focused on retail and small businesses, although it is planning to expand its corporate and investment banking business. In its 2023 annual report, Wells Fargo says its overall investment banking share has improved, moving up from number 8 in 2019 to number 6, with a 3.7% share. Despite the improvement, this is a modest market share, and there is an opportunity to increase it.
Charles Scharf – CEO of Wells Fargo, said:
“We always told people we’re Main Street. We’re not Wall Street. It’s about kitchen tables, not league tables.”
Now, Charles Scharf plans to grow Wells Fargo’s Wall Street business i.e. investment banking, advisory, and underwriting business to its existing customer base.
2. Commercial & Industrial Lending
Commercial and industrial lending is a growing area of financial services and Wells Fargo has an opportunity to regain some lost market share in this sector that is .
Net interest income, a key measure in the commercial lending sector, is projected to have a CAGR of 4.3 percent between 2024 and 2029, reaching more than $4.06 trillion US by the end of that term.
Even though the company is a leader in SME lending, it can regain its leadership of commercial and industrial (C&I) lending. Wells Fargo was the largest C&I lender but lost market share in the sector to competitors.
3. Digital Infrastructure Strategy
Technology provides an opportunity for easier-to-use and more efficient products, which will enhance the customer experience. But technology isn’t just changing banking from a customer perspective. It can also lead to improved efficiency and reduced costs.
According to Gartner, IT spending for banks and investment services reached $652 billion in 2023. That was up from $603 billion the year before, and the trend is likely to continue.
Wells Fargo has partnered with Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud to move from traditional mainframe to multi-cloud technologies, thereby accelerating its digital transformation journey. This transformation, which will provide sophisticated artificial intelligence, analytics, and increased employee collaboration, must continue at a rapid pace in order to reap the benefits of new technology.
4. Expand Operations in Emerging Economies
The bank can expand its operations in emerging economies such as China, Africa and Asia to exploit growth opportunities. In China, for example, the net interest income from banking is expected to be more than $4 trillion US.
Wells Fargo’s overseas operations, which provide corporate lending services, can be expanded to provide banking services to consumers or small business customers.
Wells Fargo has branches in 35 countries and operates in several regions outside the U.S., including Canada, Europe, the Asia Pacific region, Latin America, the Middle East, Africa, India, and the Philippines. About 95% of Wells Fargo’s assets are still in the U.S., while all the other countries account for the remaining 5%.
| Regions | FY 21 Assets ($Trillion) | % Share |
| United States | 1.84 | 94.9% |
| International | 0.1 | 5.1% |
| Total | 1.94 | 100% |
Wells Fargo’s Threats
From big competition to big issues with consumer perception and trust, Wells Fargo faces its share of threats.
1. Global Economic Fluctuations
While the risk of a global recession is minimal, according to the International Monetary Fund, it cautions that economic recovery is slow and varies among regions.
Economic uncertainties can adversely affect Wells Fargo as customers default on their loans and mortgages.
2. Public Perception
Once the public’s trust has been lost, It is very difficult to get back.
With so many scandals affecting Wells Fargo, the bank can lose customers and billions of dollars in deposits, even in the case of unproven allegations.
3. Pandemic
Success and stability in the banking sector relies heavily on businesses and ordinary individuals.
Wells Fargo’s profits dropped by 89% after job losses and small business collapses due to the pandemic led to the accumulation of unpaid loans.
4. Asset Cap
As part of the punishment for the scandal involving fake accounts, the Federal Reserve imposed an asset cap of $1.95 trillion.
The Federal Reserve did ease some restrictions on Wells Fargo, allowing the company to be part of a nationwide effort to deliver billions of dollars in government-backed loans to struggling small businesses. However, the asset cap remains in place.
5. Ongoing Investigations
Whenever a company is found guilty of malpractice, regulatory bodies and others tend to scrutinize its operations more vigorously. Wells Fargo and some of its competitors are under investigation for how they handle complaints from users of the Zelle peer-to-peer payment platform. US Senate Subcommittee on Investigations chair Richard Blumenthal accused the banks, including Wells Fargo, of failing to protect consumers from “rampant scams.”
Wells Fargo also faces a class-action lawsuit over the fake accounts scandal, claiming it has not done enough to help consumers hurt by the case.
6. Intense Competition in the Banking Sector
The banking sector is dynamic and highly competitive, with players moving up and down in rankings regularly as competitors get stronger. Wells Fargo lost market share in commercial and industrial lending to JP Morgan and Bank of America.
References
- Politico (2020, April 8) Fed Eases Wells Fargo Growth Cap
- Forbes Ranking (2020). Companies Profile: Wells Fargo.
- Nivedita, C. (2020, May 4). Wells Fargo receives an ‘outstanding’ rating for community lending. Reuters
- Williams, P. (2020, February 22). Wells Fargo to pay $3 billion over fake account scandal. NBC News
- Weinstein, A. (2020, April 8). Wells Fargo small business clients miss out on billions in aid due to scandal punishment. The Charlotte Observer
- Ensign, R. L. (2020, January 11). ‘We Need to Be a Technology Company.’ Wells Fargo Struggles With Aging Systems. The Wall Street Journal
- Glazer, E. (2019, January 30). Wells Fargo Is ‘Working Hard’ to ‘Rebuild Trust.’ The Wall Street Journal
- Moise, I. (2020, January 14). Wells Fargo’s new chief pledges more cost cuts as profit slumps. Reuters
- Great Speculations (2018, June 7). Largest U.S. Commercial Banks Continue To Lose Market Share In The Mortgage Industry.
- Rothnie, D. (2020, January 17). Wells Fargo is building out its investment bank in Paris. E Financial
- Cox, J. (2018, April 13). Here’s why bank stocks are getting hit even after their earnings beat the Street. CNBC
- Egan, M. (2018, October 10). Wells Fargo customers are fed up. They could yank billions of dollars in deposits. CNN Business
- Eisen, B. (2020, April 14). Wells Fargo Profit Drops 89% as it Girds for Soured Loans. The Wall Street Journal
- Ackerman, A. (2020, April 8). Fed Eases Wells Fargo’s Asset Cap to Lend to Small Businesses Harmed by Coronavirus. The Wall Street Journal
- Gandel, S. (2020, May 6). Wells Fargo faces government investigations into its PPP loans. CBS News
- Henry, D. (2018, April 17). Wells Fargo loses steam in commercial lending as rivals pounce. Reuters.
- Wells Fargo (2023) Annual Report
- CNN (2023, September 15) Wells Fargo Exec Charged
- Wikipedia (2023, September) List of Largest Banks in the United States.
- Wikipedia (Retrieved 2024, May 23) Wells Fargo
- International Monetary Fund (2024, April) World Economic Outlook
- Senate Subcommittee on Investigations (2024, May 20) Hearing on Failure of Zelle and Big Banks to Address Deluge of Scams and Fraud
- Brand Finance (2024) Banking 500
- US News & World Report (2024, May 21) 9 of the Biggest Financial Fraud Cases in History
- Statista (2024, March) Number of employees at Wells Fargo from 2009 to 2023
- Statista (2024, June) Investment Banking Worldwide Outlook, Commercial Banking Outlook
- Gartner (2023, June) Banking IT Spending Forecast
- Statista (2024, June) Market Insights – Banking in China
- Featured Image by Jack Cohen
Tell us what you think? Did you find this article interesting?
Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below.












Add comment