Company: Amazon
CEO: Andrew Jassy
Founders: Jeff Bezos
Year founded: 1994
Headquarter: Seattle, Washington, US
Number of Employees (2020): 1,298,000
Type: Public
Ticker Symbol: AMZN
Annual Revenue (Dec 2020): $386 billion
Profit | Net income (Dec 2020): $21 billion
Products & Services: Media | Apparel | Baby Products | Consumer Electronics | Beauty Products | Gourmet Food | Groceries | Health and Personal-Care | Industrial & Scientific Supplies | Kitchen Items | Jewelry and Watches | Lawn and Garden Items | Musical Instruments | Sporting Goods | Home Improvement Tools | Automotive Tools & Accessories | Toys & Games.
Competitors: Walmart | Home Depot | Target | Alibaba Group | Oracle | Microsoft | IBM | Google | Apple | eBay | Netflix | Salesforce | Flipkart | Costco |
Fun Fact – Did you know that Jeff Bezos founded Amazon from a garage of his rented home in Bellevue, Washington?
Amazon (e-commerce giant) is one of the most recognized companies in the world for a reason. From a garage of Bezos’ rented home in Bellevue, Amazon grew rapidly to become the largest online retailer in the world.
According to Forbes 2021 ranking, Amazon was ranked:
- #2 Top Company in Sales
- #4 World’s Most Valuable Brands
- #4 World’s Best Employers
- #16 Top Regarded Companies
With over 200 million prime subscribers and one hundred million different products offered in over 50 countries across the world, we can surely learn a lot by analyzing how Amazon conducts its business.
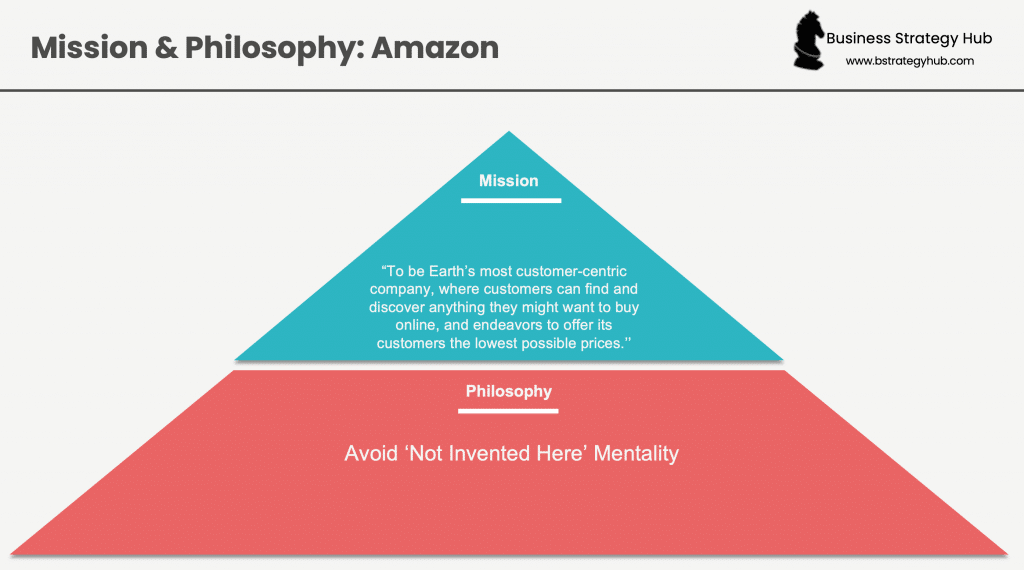
Amazon’s Mission Statement
“To be Earth’s most customer-centric company, where customers can find and discover anything they might want to buy online, and endeavors to offer its customers the lowest possible prices.”
What it means;
Amazon’s mission statement consists of four strategic components;
1. Customer Centrism: From convenience to comfort, easy execution of tasks, and useful products, Amazon is obsessed with addressing customers’ needs.
Amazon’s obsession with the customer also delivers the best user experience (UX) and customer experience (CX) through its e-commerce website, which is user-friendly, highly-responsive, and optimized for mobile. It considers customers as the bloodline and the most important stakeholder group to its online retail business.
2. The Widest Variety of Products: The third component indicates Amazon’s determination to provide customers with the widest variety of products. From apparel to consumer electronics, jewelry, gardening tools, and toys, Amazon offers a wide variety of products.
Although it already offers more than other stores, Amazon is focused on availing all other products and services on its platform and transform it into a one-stop-shop.
3. Lowest Prices: The fourth and last component in Amazon’s Mission Statement is “to offer its customers the lowest possible prices.” Currently, Amazon’s prices are lower compared to most other retailers.
The e-commerce giant has set the standard in providing customers value for money for other retailers to follow.
4. Global Reach: Amazon is focused on international leadership in the e-commerce market. Currently, Amazon offers its services in different countries across the world.
Therefore, the retailer is committed to expanding its e-commerce platform to cater to consumers in the countries not yet covered. Amazon’s strategic objective is to expand globally to offers each consumer the option to shop online for anything from anywhere across the world.
Amazon’s Leadership Principles
Amazon’s achievements can be traced back to its founder and CEO, Jeff Bezos. His leadership principles have been adopted from the executive level down to the low-level employee. These leadership principles include:
- Customer Obsession: Amazon’s leadership is immensely obsessed with satisfying the customer, evidenced by customer-centric strategies adopted by the retailer since its founding. From a high level of convenience offered by its delivery service to customer-centric return policies, Amazon is undeniably one of the most customer-obsessed companies.
- Ownership: Regardless of position, all leaders should act like they truly own Amazon. This leadership strategy ensures that all leaders put the interest of the company first by advancing long-term values rather than sacrificing them for selfish short-term results.
- Invent and Simplify: Innovation is a desired trait in leadership. The brick and mortar were accepted as the primary point of sale (POS) until Amazon arrived at the scene and asserted that virtual stores could also be the primary point of sale.
- Guts and Instincts: Leaders are born. The retailer requires leaders to tap into their strong judgment and good instincts by seeking diverse perspectives to disconfirm misguided beliefs and deliver highly accurate decisions consistently.
- Learn and Grow: Continuous improvement is what sets apart great leaders from average leaders. Amazon urges its leaders to push the boundary of self-improvement by seeking out opportunities to learn
- Hire and Develop the Best: Amazon is not your average company; it is Amazon. To this end, those tasked with the leadership of the respective department and sectors have to seek out and hire the best raise the performance bar with every hire and promotion.
- The Highest Standards: Amazon requires its leaders to insist relentlessly for the highest standards. Any person in a leadership position has to continually raise the bar regardless of whether others think it is unreasonably high.
- Think Big: The easiest way for a leader to set their teams permanently on the path to failure is to think small. It is not only a self-fulfilling prophecy but also defeats the purpose of leadership. If a leader thinks small, the team will surely be better off without this kind of destructive leadership.
- Bias for Action: When it comes to business matters, speed and timing are equally important. But in a rush to beat competitors to the punch, leaders have to acknowledge the irreversibility of their actions and take caution each step of the way.
- Frugality: Leaders are required to reinvent their strategies to address urgent issues regardless of the availability of resources to execute the task. Leaders accomplish more with less, which fuels innovation, resourcefulness, and self-sufficiency.
- Earn Trust: Trust is bestowed based on one’s position or title within Amazon, but it earned. Earning the trust of employees and customers requires leaders to listen attentively, speak passionately, and treat every person who crosses their path with uttermost respect.
- Dive Deep: From menial jobs to global strategies in Amazon’s boardroom, leaders have to be highly versatile to play different roles at all levels. Staying connected to the core functions within the company is an effective way to eradicate the misguided thought that some tasks are beneath those assigned to lead.
- Have Backbone: Leaders are nurtured by the unconventional nature of Amazon’s business, which instills immense independence in thought. Amazon is not a place for yes-men but for those with the courage to disagree even to the most normalized situation or activity by society.
- Deliver Results: The last but most important, Amazon’s leadership principle is delivering results, which coincidentally is the main purpose of leaders. From inputs to quality and deadlines, leaders have to multitask by focusing on all these key ingredients to success to deliver the desired results.
Amazon’s Philosophy
Amazon has established and nurtured a highly effective “Day 1” philosophy that has driven the company’s growth over the years and can be broken down into ten components:
- Avoid ‘Not Invented Here’ Mentality: Stakeholders can eradicate the limitation imposed by ‘not invented here’ and learn from internal and external sources to bring in new and innovative ideas. Although Jeff Bezos did not invent e-commerce, Amazon is synonymous with e-commerce.
- People Empowerment: From sellers and enterprises to content creators and developers, Amazon’s philosophy is to empower people with lucrative options to make a living. Amazon also empowers customers by providing flexible options to access cheaper products.
- The Empty Chair: In the early years, an empty chair was brought into boardroom meetings to represent the customer and ensure that their needs and desires are taken into account. Over time, the philosophy of obsessing over the customers is evident from top to bottom.
- Avoid Bureaucracy: Amazon does not subscribe to the notion of following the chain of command. Businesses can use either Type 1 or Type 2 . Type 1 are irreversible decisions, while Type 2 decisions can be reversed. Amazon uses Type 2 to allow all stakeholders to engage in decision-making without supervision.
- Calculated Risk-taking: Amazon values calculated risk-taking. The founder believes that “failure and invention are inseparable twins” and has nurtured a strong experimentation culture as a process of attaining inventive and innovative ideas.
- Build the Right Culture: Amazon has built a breakneck-paced and cost-conscious culture that is perfectly suited for its time-sensitive Over time, all stakeholders gradually became instinctively aware of the importance of timely and cost-effective operations.
- Shared Economy: Instead of developing your own e-commerce website, you can use Amazon’s platform as a service (PaaS). Amazon’s shared economy philosophy has enabled millions of people around the world to set up virtual stores.
- Respect to All: From hiring for diversity to global presence, Amazon emphasizes the value of treating every person with respect by offering everyone equal opportunity to pursue their dreams and aspiration.
- Never Settle: Even though delivering millions of packages worldwide is impressive, all that does not matter if even 1% of the packages were late or undelivered. Amazon will never settle for 99% and is not satisfied until it is 100%.
- Own It: All stakeholders are owners.
References & more information
- Featured image by Christian Wiediger on Unsplash
- Amazon: Annual Report
- Mohsin M. (2019, August 29). 10 Amazon Statistics You Need to Know in 2020. https://www.oberlo.com/blog/amazon-statistics
- Culture. https://www.amazon.jobs/en/working/working-amazon Accessed on April 11, 2020
- https://www.forbes.com/companies/amazon/?list=global2000#31ef0c06fb89
- Our Global Offices. https://www.aboutamazon.com/working-at-amazon/our-global-offices Accessed on April 11, 2020
- De Groot, E. (2019, February 22). What I Learned from Amazon’s Jeff Bezos: How to Stay Customer-centric. https://www.revelx.co/blog/amazon-customer-centric/ Accessed on April 11, 2020
- Debter, L. (2019, May 15). Amazon Surpasses Walmart as the World’s Largest Retailer. Forbes. https://www.forbes.com/sites/laurendebter/2019/05/15/worlds-largest-retailers-2019-amazon-walmart-alibaba/#2e4fb6684171 Accessed on April 11, 2020
- Del Rey, J. (2019, Oct 14). Amazon’s new weapon to crush competition: $1 items delivered for free. VOX. https://www.vox.com/recode/2019/10/14/20906728/amazon-prime-low-price-products-add-on-one-day-delivery Accessed on April 11, 2020
- Our Leadership Principles. https://www.amazon.jobs/en/principles Accessed on April 11, 2020
- Lenzner, R. (2018, April 24). Amazon Celebrates 20 Years of Stupendous Growth As Earth’s Most Customer-Centric Company.
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/robertlenzner/2018/04/24/amazon-celebrates-20-years-of-stupendous-growth-as-earths-most-customer-centric-company/#313cbd1e44dc
- AWS Amazon. Our Culture. https://aws.amazon.com/careers/culture/
- Rodriguez, A. (2018, November 28). The bulk of Amazon’s ad dollars are coming from placement in its virtual store aisles. https://qz.com/1477516/amazon-gets-most-of-its-ad-revenue-from-its-virtual-store/
- Stoll, J. D. (2019, Oct. 18). ‘Feel the Force’: Gut Instinct, Not Data, Is the Thing. Amazon Blogspot. https://amazon-store-business.blogspot.com/2019/10/feel-force-gut-instinct-not-data-is.html
- Scott, A. (2019, July 11). From The Warehouse To IT: Amazon Offering 100,000 Workers Tech Training. https://www.npr.org/2019/07/11/740660070/from-the-warehouse-to-it-amazon-offering-100-000-workers-tech-training
- Mautz, A. (2019, Nov. 6). Amazon’s ’50 Percent Rule’ Will Help You Avoid the 5 Biggest Interviewing and Hiring Mistakes. https://www.inc.com/scott-mautz/amazons-50-percent-rule-will-help-you-avoid-5-biggest-interviewing-hiring-mistakes.html
- Hyder, S. (2020, Mar. 19). Competing Against Amazon? Here Are 5 Things Every ECommerce Company Should Know.
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/shamahyder/2020/03/19/competing-against-amazon-here-are-5-things-every-ecommerce-company-should-know/#42b91d245652
- Jennifer, I. (2019, Mar. 1). How to answer Amazon “Think Big” interview questions. Interview Genie. https://interviewgenie.com/blog-1/2019/3/1/how-to-answer-amazon-think-big-interview-questions
- Haden, J. (2018, Dec. 3). Amazon Founder Jeff Bezos: This Is How Successful People Make Such Smart Decisions. https://www.inc.com/jeff-haden/amazon-founder-jeff-bezos-this-is-how-successful-people-make-such-smart-decisions.html
- Duhigg, C. (2019, October 10). Is Amazon Unstoppable? The New Yorker. https://www.newyorker.com/magazine/2019/10/21/is-amazon-unstoppable
- Anderson, D. (2017, Jun 25). Interviewing at Amazon — Leadership Principles. Medium. https://medium.com/@scarletinked/are-you-the-leader-were-looking-for-interviewing-at-amazon-8301d787815d
- Peter, E. (2019, Nov. 8). These 14 Amazon Leadership Principles Can Lead You and Your Business to Remarkable Success. https://www.inc.com/peter-economy/the-14-amazon-leadership-principles-that-can-lead-you-your-business-to-tremendous-success.html
- Rosoff, M. (2019, Dec. 13). Amazon will be the most important company in the 2020s. CNBC. https://www.cnbc.com/2019/12/13/amazon-will-be-the-most-important-company-of-the-2020s.html
- Lee, D. (2020, January 31). Amazon shares leap after delivering bumper holiday sales. Fortune. https://www.ft.com/content/0c758b8c-4396-11ea-a43a-c4b328d9061c
- (2017, Apr. 21). What Is Jeff Bezos’s “Day 1” Philosophy? Forbes. https://www.forbes.com/sites/quora/2017/04/21/what-is-jeff-bezos-day-1-philosophy/#49fb39161052
- Madden, D. (2018, September 25). Jeff Bezos Says It’s Always Day 1 at Amazon. https://www.inc.com/debbie-madden/jeff-bezos-says-you-should-treat-every-day-at-your-company-like-day-1-heres-why-hes-wrong.html
- Scott M. (2019, July 16). Jeff Bezos Says the Very Best Leaders Empower Others In This 1 Way. Inc. https://www.inc.com/scott-mautz/jeff-bezos-says-very-best-leaders-empower-others-in-this-1-way.html
- Patel, N. (2018). 12 Business Lessons You Can Learn from Amazon Founder and CEO Jeff Bezos. Neil Patel. https://neilpatel.com/blog/lessons-from-jeff-bezos/
- Hern, A. (2017, Apr. 24). The two-pizza rule and the secret of Amazon’s success. The Guardian. https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2018/apr/24/the-two-pizza-rule-and-the-secret-of-amazons-success
- Thompson, S. (2017, Aug. 29). Jeff Bezos Just Explained How to Achieve Customer Loyalty in Only 1 Sentence. Inc. https://www.inc.com/sonia-thompson/in-1-sentence-jeff-bezos-explains-the-philosophy-e.html
- Kantor, J., and David Streitfeld (2015, Aug. 15). Inside Amazon: Wrestling Big Ideas in a BruisingWorkplace.TheNewYorkTimes. https://www.nytimes.com/2015/08/16/technology/inside-amazon-wrestling-big-ideas-in-a-bruising-workplace.html
- McCracken, H. (2019, Dec. 4). These are Amazon’s 38 rules for success. Fast Company. https://www.fastcompany.com/90334069/these-are-amazons-38-rules-for-success
- Mullaney, T. (2017, January 25). 5 key business lessons from Amazon’s Jeff Bezos. https://www.cnbc.com/2016/05/13/5-key-business-lessons-from-amazons-jeff-bezos.html
Tell us what you think? Did you find this article interesting?
Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below.











Add comment