Company: United Parcel Service (UPS)
CEO: Carol Tomé
Founder: James E. Casey
Year founded: August 28, 1907
Headquarters: Atlanta, Georgia
Employees (FY2019): 495,000
Ticker Symbol: UPS
Type: Public
Annual Revenue (FY2019): $ 74.09 Billion
Profit | Net income (FY2019): $ 4.44 Billion
Products & Services: Transportation | Distribution | Contract Logistics | Ground Freight | Ocean Freight | Air Freight | Customs Brokerage | Insurance | Financing | Supply Chain Management
Competitors: FedEx | DHL International | Kuehne + Nagel | CEVA Logistics | Blue Dart | Royal Mail | C.H. Robinson | Deutsche Post | DB Schenker | GLS | XPO Logistics | Purolator | YRC Freight
Fun Fact: Did you know that Frederick Wallace Smith wrote the concept behind FedEx as a term paper when he was an undergrad at MIT?
Only a handful of companies can operate successfully in an industry for over a century with UPS being one of the chosen few. The company has gone through some of the worst economic periods in history and emerged stronger.
By employing highly effective strategies throughout its long and illustrious operations, UPS grew to become the largest logistics and delivery service company.
We can learn a lot by assessing UPS’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Here is the UPS SWOT analysis.
UPS Strengths
- Strong Global Presence: UPS expanded its UPS Worldwide Express and UPS Express Plus to 40 countries part and now offers time-definite delivery shipments to businesses across 140 countries and territories. Additionally, it operates small delivery services in more than 220 countries under International Package operations.
- Online Tracking: UPS has one of the most advanced online tracking capabilities in the industry, which tracks 295 million deliveries per day.
- SMART Network: Effective delivery operations relies on seamless integration of collection and distribution mechanisms. UPS invested $20 billion to build its Southeast Metro Automated Routing Terminal (SMART) logistics network facility in Atlanta, which connects all systems and equipment in its entire network.
- Excellent Customer Service: To attract, satisfy, and retain customers, businesses have to deliver high-quality service consistently, which is particularly important in the delivery service. UPS offers excellent customer service and has higher customer satisfaction than FedEx.
- Highly Innovative: Delivering parcels globally on time requires immense innovation. To deliver each package on time, the Chief Information Officer of UPS developed a smart logistics network and won the Forbes CIO Innovation Award.
- Fast Deliveries: Timely deliveries consistently is a major strength. UPS streamlines its operation with simple handheld devices for communication, scanning packages, customer signatures as well as complex automation like its GPS navigation and reroute technology. All these operational strategies ensure UPS delivers faster than competitors.
- Competitive Prices: Offering high-quality service at affordable prices is the most effective way to attract and retain customers. In the logistics and delivery service, UPS offers competitive prices for overnight shipping and across all other different categories.
UPS Weaknesses
- Reliance on US Market: Even though UPS operates globally, it relies heavily on the US market. In 2019, US domestic package delivery and freight generated $58.6 billion while international delivery brought in $15.41 billion. If the US market slows down due to recession, UPS will be adversely affected.
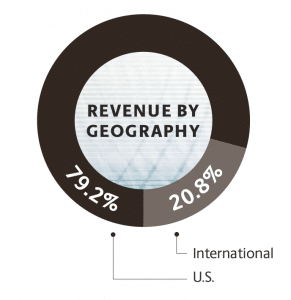 Image source: UPS Annual Report
Image source: UPS Annual Report - Adverse Financial Impact during Peak Holiday Season: For UPS to keep up with demand and deliver on time during high peak online shopping season, it has to spend way more than normal periods. The huge amount spent to handle as much as double the average daily package volume affects the profitability of the company to reap the maximum benefits offered by peak holiday seasons.
- Operational Issues: The management has been postponing upgrades of equipment and delivery systems for decades. Using 19th-century infrastructure to operate in the fast-moving world of the 21st century is increasingly becoming a challenge but upgrading the system costs $20 billion, which is about 5-year worth of UPS profits.
- Poor Employee Safety: Poor and unsafe work environment undermine the morale, efficiency, and productivity of employees. There are several cases of UPS employees being injured and one employee passed away after contracting the Covid-19 virus.
- Burdening Purchased Transportation Costs: The delivery business is influenced immensely by transport costs. Purchased transportation cost is incurred when UPS uses third-party transportation carriers. Around 19% of UPS operating expense is directed to purchased transportation in the fiscal year 2019. If transport costs continue to increase, UPS can lose its profitability.
UPS Opportunities
UPS has emerged as a leader in the drone delivery field due to its recent partnerships and progressive approach in adapting to innovations and the latest technologies. https://t.co/NLq8nO46Am
— Felisindo Gonzalez (@FelisindoGonza2) October 5, 2020
- Drone Testing: UPS has been testing and expanding its drone delivery capabilities. UPS tested its drone delivery technology at Wake Med hospital campuses, transporting lab samples across different hospital campus buildings.
- Strengthen e-Commerce Operations: The E-Commerce sector is growing rapidly with new players getting into the business constantly. This sector relies on delivery services, which UPS can exploit by strengthening its e-Commerce operations and services.
- Expand through Mergers and Acquisition: Mergers and acquisitions allow companies to expand quickly into new markets. Even though UPS failed to capture the European market fully after the collapse of its bid to merge with TNT Express, it can acquire small European logistics companies to increase its market share.
- Diversify Portfolio: There are 3 primary business segments in UPS operations. For instance, it can diversify into the B2C ecommerce retail sector, supporting Small and Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs) and use its extensive global networkagainst competitors.
According to the fiscal year 2019 report, UPS revenue share of its 3 primary business segments are as follows:- Domestic Package: 62.7% ($46.49 Billion)
- International Package: 19.2% ($14.2 Billion)
- Supply Chain & Freight: 18.1% ($13.38 Billion)
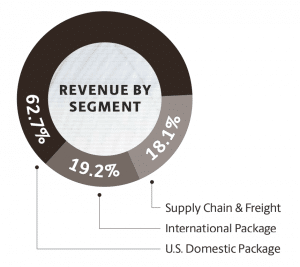 Image source: UPS Annual Report
Image source: UPS Annual Report
- Expand the target market: UPS operates primarily as a business delivery service (B2B and B2C) for online retailers like Amazon even though the number of ordinary consumers using delivery services is increasing rapidly. The company can fuel its growth by expanding its target market to include ordinary consumers.
- Expand to 7-Day Delivery: UPS has started a 7-day delivery service. Earlier, UPS pickup and delivery service operated for 6 days (Monday – Saturday). With the surge in online shopping and high customer expectations, now UPS has included deliveries on Sundays.
UPS Threats
- Intense Competition: With stiff competition from FedEx, DHL, Amazon, YRC, Old Dominion, and many more, the market share and profits of UPS are always under threat.
- Over-reliance on one customer “Amazon”: Ecommerce giant – Amazon represented about 11.6% of UPS revenue in the fiscal year 2019. As Amazon is gearing up to compete in delivery and transportation service, UPS revenue can be at risk due to any change in their relationship.
- Trade Tensions: As a global operator, the stability, sustainability, and profitability of UPS rely on revenues from different regions. This makes trade tensions a major threat to the company.
- The threat of Strike: Even though UPS employees have not gone on strike since 1997, the risks and challenges of working through the pandemic coupled with several contractions are fueling anger and frustration in the workforce. Even a short strike can cost the company millions.
- Looming Recession: The pandemic has left devastation and destruction across the world with several countries already deep into recession. UPS pulled its 2020 earnings forecast after posting a 13% drop in profit in the first quarter. If the recession is severe, the company will experience a larger decline in profits.
- Global Pandemic: UPS earning is projected to decline by 7% in full year 2020 as the pandemic brought the entire world to a halt. If there is a second wave, UPS could lose even more.
References
- UPS (2019, December 9). UPS Expands Global Footprint Of International Express Services. Globe Newswire
- Pressman, A. (2019, December 20). UPS’s $20 billion bet on e-commerce is paying off. Fortune
- Vanamburg, D. (2018, March 28). UPS tops FedEx in customer satisfaction, as Amazon appears on the horizon. ACSI Matters.
- High, P. (2019, December 11). UPS Tech Chief Wins Forbes CIO Innovation Award By Developing a Global Smart Logistics Network. Forbes
- Woyke, E. (2018, February 16). How UPS delivers faster using $8 headphones and code that decides when dirty trucks get cleaned. MIT Technology Review.
- Wang, J. (2020, March 10). The Cheapest Overnight Shipping Options: USPS vs. UPS vs. FedEx. Wallet Hacks
- Brennan, M. (2017, January 31). The surprising way an online shopping surge crushed UPS earnings. CNBC
- Ziobro, P. (2018, June 15). UPS’s $20 Billion Problem: Operations Stuck in the 20th Century. The Wall Street Journal
- Baertlein, L. (2020, April 7). UPS employee dies of COVID-19 infection in Kentucky. Reuters
- UPS Flight Forward Attains FAA’s First Full Approval For Drone Airline
- Bray, C. (2018, February 26). UPS Seeks more than $2 Billion in Damages over TNT Bid. The New York Times
- UPS (2019, October 21). UPS Strategy Transforms E-Commerce Through Alliances And Agreements. Global Newswire
- Ziobro, P. (2019, July 23). With an eye on Amazon, package company joins FedEx in boosting frequency. The Wall Street Journal
- Shivdas, S. (2020, April 28). United Parcel Service pulls 2020 forecast on pandemic uncertainties. Reuters
- Is UPS Stock A Buy Amid Coronavirus E-Commerce Boom?
- Costa, K. (2020, April 7). “We aren’t going to take it anymore:” Anger among UPS workers as Teamsters union seeks to rein in logistics strike wave. World Socialist Web
Tell us what you think? Did you find this article interesting?
Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below.












Add comment