Fintech companies are changing the way individuals and businesses send and receive payment. They facilitate cross-border payments, support online transactions, eliminate the middlemen involved, and empower millions. To put this into perspective, PayPal, one of the top fintech companies in the US, boasts 426 million accounts across 200 markets. But what is PayPal’s business model, and how does it earn revenue?
What is PayPal?
Founded in 1998 by Peter Thiel, Luke Nosek, Max Levchin, Yu Pan, and Ken Howery, PayPal is a technology platform specializing in online payment systems focusing on simplifying digital payments, boost person-to-person transactions, and offer businesses more economic opportunities on a global scale.
PayPal Customer Segmentation
PayPal primarily caters to three customer segments:
- Retail customers: With over 391 million active customer accounts, PayPal is a top choice for individuals to shop online, send or receive money, and purchase or sell items on eBay.
- Businesses: PayPal is a fintech platform that empowers small businesses and enterprises to expand their reach globally, explore new selling mediums, and give their customers the choice to pay however they want. As such, PayPal powers around 35 million active merchant accounts.
- Partners and developers: Businesses requiring an end-to-end payment platform to suit their varied needs partner with PayPal. On the other hand, PayPal caters to developers through resources like SDKs and APIs, making it easier for them to integrate the payment platform with their existing or new solutions.
PayPal supported over 25 billion transactions internationally and had a total payment volume (TPV) of $1.53 trillion in 2023. But why do individuals, businesses, and developers use this payment platform? Let’s find out.
PayPal’s Value Propositions
PayPal’s unique value propositions for its customers and partners include the following:
1. Convenient and secure
PayPal’s biggest draw for individuals is its convenience. It simplifies and provides a secure environment for national and international transfers via its products, including PayPal, Venmo, and Xoom.
2. Supports multiple funding sources
PayPal allows customers to add money to their digital wallets from their bank accounts, credit cards, debit cards, PayPal and Venmo account balances, PayPal’s consumer credit products, specific cryptocurrencies, gift cards, and rewards.
3. Facilitates buy now, pay later
PayPal facilitates buy now, pay later (BNPL) as part of its credit offerings in specific markets, such as the UK, the US, France, Germany, and Japan (through Paidy). While this feature might seem like any other BNPL offering, PayPal stands out because it doesn’t levy interest or charge its customers late fees if they miss their payments.
Moreover, the brand offers installment options to consumers in the US (via private financial institutions) and Germany. It also provides PayPal and Venmo credit cards in the US in partnership with a private financial organization. PayPal Credit is available in the UK, too.
4. Empowers merchants and their businesses
PayPal empowers merchants and businesses to accept online payments. Moreover, it offers merchants access to its credit range. Merchants can also take advantage of its fraud prevention and risk management programs and offset losses using the company’s dedicated protection solutions. That’s not all. Businesses can convert their leads more effectively using data analytics and tailored tools.
5. Merchants can accept online and in-person payments
PayPal encourages merchants to accept in-person and online payments. Digital payments can be made using PayPal or Venmo wallets, credit and debit cards, consumer credit solutions, and other online wallets.
6. Merchant financing
The financial technology company offers merchant financing through PayPal Working Capital and PayPal Business Loan. With the working capital option, businesses receive a cash advance based on their annual payment volume processed. Alternatively, companies can use short-term loans if they opt for the business loan option.
Who are the Key Partners of PayPal?
PayPal’s partners have helped propel the company to success. Its key partners include:
- Investors: PayPal’s investors help keep the company afloat.
- Financial institutions: PayPal partners with multiple financial institutions to further its credit offerings.
- Security partners: PayPal values its customer’s privacy and security with focus on providing an ecosystem where their customer’s personal data remains safe, and is protected against digital frauds and scams. To illustrate, the fintech company partnered with the BBB (Better Business Bureau) Institute for Marketplace Trust, the educational foundation of BBB Institute, to prevent fraud.
- Customers and merchants: Several individuals, merchants, and enterprises use PayPal to transfer funds seamlessly.
- Strategic partnerships: Paypal partners with several other businesses to grow and expand its business. Example includes PayPal’s multi-year partnership deal with Uber. Similarly, PayPal partnered with Salesforce to make it easier for businesses to expand globally and enhance the ecommerce experience for their customers. The company also partnered with famous American brands, like Amazon, Starbucks, DoorDash, Target, Sephora, Uber, and Chipotle, to roll out gift cards for Venmo.
- Celebrity partnerships: The multinational company entered into a multi-year deal with Chrissy Teigen’s lifestyle brand Cravings to offer BNPL options to online customers.
- Social impact partners: The multinational company partners with several organizations, like the Anti-Defamation League (ADL), to offer social relief. It even partnered with Meta to facilitate donations through Instagram and Facebook in the US, UK, Australia, and Canada.
- Technology partners: These partners help the platform run without glitches and roll out new features or products.
What are PayPal’s Key Resources?
PayPal’s key resources include:
- PayPal’s website and mobile app are its most significant resource.
- Profitable partnerships and strategic investments across the globe.
- PayPal’s ecosystem of over 27,200 employees globally.
- Intellectual property rights, like trademarks, domain names, patents, copyrights, trade dress, and trade secrets.
- Excellent brand image in the financial technology sector.
What are PayPal Channels?
Customers can access PayPal through its website. It also has dedicated apps to serve Android and iOS users, which can be downloaded through the App Store and Google Play.
Additionally, the fintech company is active on multiple social channels—X (formerly Twitter), LinkedIn, Instagram, and Facebook—and leverages it to engage with its customers and partners.
How does PayPal Maintain Customer Relationships?
PayPal customers can sign in and visit the Help Center to get their queries answered. They can also contact customer service for speedy grievance redressal.
What is PayPal’s Cost Structure?
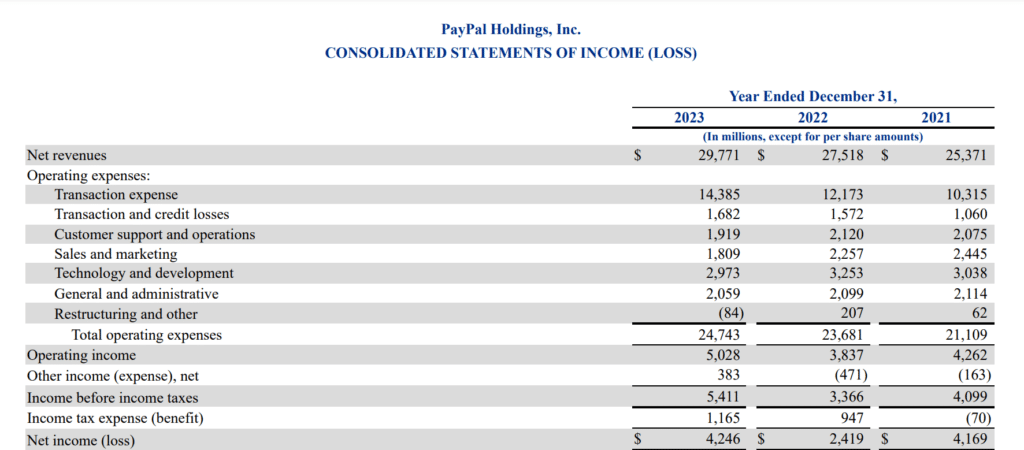
PayPal’s total operating expense was approximately $24.7 billion for the fiscal year ending December 31, 2023.
It incurred $14 billion in transaction expenses, $1.6 billion in transaction and credit losses, $1.9 billion in customer support and operations, $1.8 billion in sales and marketing, $2.9 billion in technology and development, $2.06 billion in general and administrative expenses, and ($84) billion in restructuring and other costs.
How Does PayPal Generate Revenue?
PayPal’s net revenue was around $29.7 billion for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2023.
But how does PayPal make money? Let’s find out.
PayPal’s revenue streams can be categorized into two sections:
1. Transaction revenues
PayPal’s main source of income is the transaction fees it charges customers when they receive money on the platform. It also charges fees on currency conversion, international transfers, and fund transfer from PayPal or Venmo wallet to bank accounts, and crypto transactions.
2. Revenue from other value-added services
Revenue from other value-added services includes income generated from partnerships, referrals, subscriptions, gateway fees, and services offered to customers. Interest and fees from loans and underlying assets are also included under this category.
The Bottom Line: PayPal Supports Financial Freedom
PayPal is rapidly changing the way individuals and corporations transfer funds. Its ease of use, convenience, security and affordability make it a top choice for individual consumers, merchants, and corporations alike.
References & more information
- eveloper Resources PayPal 10-K
- PayPal
- Find out Why Millions of Shoppers Use PayPal | PayPal RO
- PayPal for Business | Merchant Services | PayPal RO
- Partner & Developer Resources – PayPal
- PayPal Commerce Platform for Platforms & Marketplaces
- News | PayPal Newsroom
- BBB Institute for Marketplace Trust Partners with PayPal
- Press Release: Uber and PayPal Expand Relationship
- Press Release: Introducing Gift Cards on Venmo
- PayPal Deepens Relationship with Salesforce to Help Global Merchants Optimize their Ecommerce Experience
- Cravings by Chrissy Teigen Selects PayPal as Exclusive Buy Now, Pay Later Partner to Build Lifestyle Brand
- Press Release: PayPal Partners with ADL to Fight Extremism and Protect Marginalized Communities – July 26, 2021
- PayPal Partners with Meta to Enable Donations on Facebook and Instagram in the US, UK, Australia and Canada
- PayPal App: Send and Manage Your Money
- PayPal Contact Us | United States
- Featured Image by Marques Thomas
Tell us what you think? Did you find this article interesting? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below.












Add comment