Company: Uber
CEO : Dara Khosrowshahi
Year founded : 2009
Headquarter : San Francisco, USA
Number of Employees (2020): 26,900
Public or Private: Public
Ticker Symbol: UBER
Market Cap (July 2020): $54.02 Billion
Annual Revenue (2020) : $14.1 Billion
Profit |Net income (2020): $-8.5 Billion
Products & Services: UberX | UberBlack | UberSUV | UberXL | UberPlus | UberPool | UberSelect | Uber eats
Competitors: Lyft | Ola Cabs | Curd | Grab | Didi Chuxing
Fun Fact:
Did you know that 87% of Uber drivers said they drive on the Uber platform because they get to be their own boss.
An Overview of Uber
Uber is headquartered in San Francisco, California and offers peer-to-peer ridesharing, taxi cab, food delivery, and transportation services. It now operates in 785 metropolitan areas worldwide. Uber platform is available through its website and mobile apps. Since its launch, the company has significantly affected the economy. The effect of Uber on other industries is known as ‘Uberization.’
The company’s name is based on the commonly used word ‘Uber’ which means ‘super’ or ‘topmost.’ The company has been able to provide quick, easy, and luxurious transportation services.
Uber introduced the ride-sharing app phenomenon. It replaced the concept of people having to step out and hire a cab for themselves. Uber has since become an all-time favorite for travelers and multiple app users. People can now book an Uber ride and have the driver come right at their door any given time. Its efficient features have inspired many other ride-sharing app services like Lyft, Ola, Didi.
Nonetheless, the company continues to grow and has become mainstream despite all the criticism and negative reviews. Currently, Uber has many opportunities to introduce new features to give it a competitive edge over its competitors. Every company has certain strengths and weaknesses. We will address these as we further discuss the business structure of Uber.
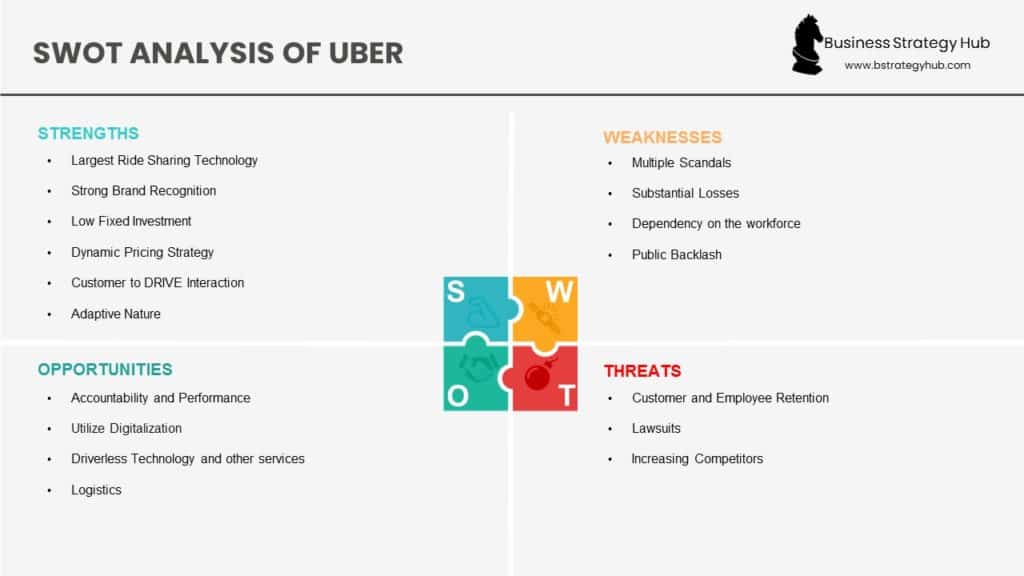
Uber SWOT Analysis
The following is the SWOT analysis of Uber:
Uber’s Strengths
-
Largest Ride Sharing Technology: Uber has positioned itself as the largest ride-sharing technology in the world. It was one of the first ride-sharing apps, operating across the globe. In 2020, Uber is available in more than 93 countries and over 900 cities, with 103 million monthly users served by a total of 5 million drivers. [1]
-
Strong Brand Recognition: Uber has maintained a strong brand recognition in over 50 countries. It has already overtaken GM, Honda, and Ford regarding brand value framework. With its incorporation of new technological features, it is predicted to enhance its services in the next few years. In 2020, Uber’s valuation stands at $75 billion. [2]
-
Low Fixed Investment: Uber operates on low fixed investment (low operational cost) and has easily accessed more cites in its communicative network. Because there is no fixed infrastructure or investment in place, the company continues to expand at a fast pace.
- Dynamic Pricing Strategy: Uber has remained consistent in its dynamic pricing strategy. It’s “Higher the Demand; Higher the Price” policy has proven to be beneficial to its drivers and industry. Its drivers earn a substantial amount at night time and during bad weather and holiday nights.
-
Adaptive Nature: The adaptive nature of Uber has great recognition across the globe. Its International exposure has allowed it to blend and integrate among different nationalities and cultures. It in turns has helped Uber to earn trust and reliability. It has received acclaim for its smart marketing. For example, the company uses its social media accounts to get in touch with customers. Through Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram Uber lets its customers know about deals, promos, and any updates. Additionally, the company also addresses the complaints of its customers through social media channels. These social media channels are great for customer engagement and quick feedback.
-
Low Prices as Compared to Taxis and Other Commute apps: Uber offers low prices as compared to traditional taxis. The biggest difference between taxis and Uber is that Taxis charge per mile (while traveling) and per minute (when not traveling). On the other hand, Uber charges per minute and per mile for both moving and idling. This pricing strategy has proven to be beneficial for customers. Additionally, Uber is cheaper than Lyft and SideCar in 20 major U.S cities. However, other variables affect the final price of a ride. These include the geographical location, distance traveled, surge pricing, cancellation fees, and other trip-specific additions.
- Customer to Driver Interaction: The business model of Uber is ideal for a customer to driver interaction. Uber has created a rating system that helps customers rate their traveling experience as well as the driver. This rating system helps identify the best drivers and monitors the performance of the drivers.
Uber’s Weaknesses
-
Multiple Scandals: Uber’s brand has received negative coverage over numerous scandals and controversies. Cases such as sexual harassment and targeted attacks have defamed the company. It came to the point that its co-founder Travis Kalanick had to resign. Public outcry over these allegations resulted in #DeleteUber campaign where about 500K users deleted their accounts in 2017.
-
Substantial Losses: Although it has increased its revenues, Uber has been facing significant losses since 2009. In order to beat out its growing competition, the company began providing bonuses to its drivers and discounts to its customers. This investment has only resulted in Uber’s net losses to exceed $2.75 billion in 2016.
-
Dependency on the workforce: Uber’s heavy dependence on its workforce and internet has not been advantageous for the company. The behavior of its drivers has been unpredictable and has damaged the image of the company. Over 103 Uber drivers in the US were accused of sexual harassment and abuse which paints a poor picture of the company culture.
-
Public Backlash: Uber faced a severe public backlash over its high pricing during Hurricane Sandy. This forced the company to revise its policy.
-
Exploitative Business Model: Multiple governments and workers’ unions are agitating for Uber to change their business model. Uber’s model misclassifies its drivers as independent contractors instead of employees, which robs them extensive benefits. Uber has been sued by Massachusetts and California for misclassifying its drivers. [3]
- Poor Working Condition: Most companies invest heavily to support their employees. On the other hand, Uber’s drivers are almost entirely on their own, which exposes them to security risks. Also, they have to bear expenses like insurance, repairs, and gas. [4]
Uber’s Opportunities
-
Accountability and Performance: Customers are no longer impressed by unorganized cab services who have been over the market. This presents a lucrative opportunity for Uber. It can improve by offering its services based on accountability and performance. By tracking the performance of the drivers, the company can identify top performers. Additionally, the company can address the numerous cases of sexual misconduct that have been reported against many Uber drivers.
-
Utilize Digitalization: The world is becoming increasingly digital. More people prefer an interconnected – network that is easily available on their smartphones. Uber should continue to invest in services like Uber Eats and expand its customer base accordingly. There are countries and places where Uber does not operate like China and Denmark. Uber can increase its customer base by expanding its operations in these areas.
-
Driverless Technology and other services: Uber has the potential to venture into driverless technology and other special transportation services like ambulances or other forms of emergency vehicles. This will help the company to differentiate, gain more popularity in public and the mainstream media.
-
Logistics: Uber can also launch its own movers and packers for the public’s convenience, They don’t have any shortage of resources after all.
-
Air Taxis: According to research by Morgan Stanley, the global market for electric air taxis or flying cars is projected to grow to $1.5 trillion by 2040. Uber has partnered with Hyundai to build flying taxi for Uber’s Elevate aerial ride-hailing service. The prototype was unveiled recently and can carry four passengers for up to 60 miles per trip at 180 mph. [5]
-
Strengthen Delivery Services: Recent events have increased demand for delivery services. Uber already offers food delivery service via Uber Eats and can strengthen this service further. In July 2020, Uber launched an app-based grocery delivery service in Canadian and Latin American cities and planned to expand the service to the U.S. [6]
-
Expand through Acquisitions: Uber recently acquired Routematch, a transit software provider. The acquisition allows Uber to expand its public transportation service. It also acquired Postmates for $2.65 billion to expand Uber Eats food delivery service and supply everyday goods. [7]
- Diversify Offerings: Transportation in urban areas has been transformed by recent events. Commuters are seeking alternative options to avoid crowded buses and trains. Uber can exploit changes in travel habits. It recently acquired Routematch in its push into the public transportation sector and is also offering its software expertise to several public transit organizations. [8]
Uber’s Threats
-
Customer and Employee Retention: With competition on the rise, customer and employee retention can prove to be a challenge for Uber. Any financial incentive from its competitor is enough to steal its customer base and employees.
-
Lawsuits: About 300,000 Uber drivers filed lawsuits against the company over the company’s minimum wage policy. These were settled out of court However, the cases were enough to threaten and damage Uber’s public image.
- Increasing Competitors: Competition from Lyft and other transportation services such as Ola in India has significantly affected Uber.
-
Stringent Regulations: Several U.S. states are enacting regulations focusing on the employment status of tens of thousands of gig workers like Uber’s independent drivers. In California, regulators ruled that all drivers should be classified as employees. Providing employee benefits to all drivers can overburden or even bankrupt Uber. [9]
-
Economic uncertainty: Recent events have created uncertainty in markets globally. Uber was forced to lay off 1000 employees in the first round and 3000 employees in the second round after trip volume reduced by 80%. Also, it has spent $19 million to assist its drivers financially. [10]
- Employees’ Strikes: Just like any service company, Uber depends heavily on its large workforce. A strike can ground its operations and affect the bottom line. In June 2020, more than 1000 food delivery drivers in Brazil participated in a strike to demand better working conditions. [11]
Conclusion
The SWOT analysis of Uber shows the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of the biggest transportation company. The future looks promising for Uber. Despite controversies, Uber can thrive through effective global expansion and marketing.
It simply needs new leadership and accountable management to handle its challenges in the future.
References & more information
- Iqbal, M. (2020, July 14). Uber Revenue and Usage Statistics (2020). Business of Apps
- Kovaleski, D. (2020, February 25). If You Invested $500 in Uber’s IPO, This Is How Much Money You’d Have Now. The Motley Fool
- Bellon, T. (2020, July 14). Massachusetts sues Uber, Lyft, over driver status as contractors. Reuters
- Nova, A. (2020, September 17). Uber drivers block traffic in Manhattan, protesting low pay and poor working conditions. CNBC
- Hornyak, T. (2020, March 7). The flying taxi market may be ready for takeoff, changing the travel experience forever. CNBC
- Bellon, T. (2020, July 7). Uber launches grocery delivery in Latin America, Canada, with the U.S. to follow. Reuters
- Hawkins, A. J. (2020, July 6). Uber acquires meal delivery service Postmates for $2.65 billion. The Verge
- Sawers, P. (2020, July 16). Uber acquires Routematch to make public transport ‘more accessible.’ Venture Beat
- Sonnemaker, T. (2020, June 10). Uber and Lyft drivers are now employees under California law. Business Insider
- Hawkins, A. J. (2020, May 18). Uber lays off 3,000 more employees in the latest round of COVID-19-inspired cuts. The Verge
- Rochabrun, M., and Gabriela Mello (2020, July 1). In Brazil, delivery drivers for Uber, Rappi,and others protest amid pandemic. Reuters,and others protest amid pandemic. Reuters
Tell us what you think? Did you find this article interesting? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below.












Very nice post! Very clear and easy to read also.
Thank you Val for the kinds words, I am glad you liked the analysis.
Looks really great! Thanks for the post.
You hit a variety of key points in this analysis i am giving you credit for your work, I used in my paper for College. The break down on the analysis was very helpful and gave me a great deal of information. I used your analysis to back up the ideas and knowledge I have already gained from working for the company.
Great Job ! !
Thanks Montrelle, glad to see it helped you for your college paper.
Happy Reading !
Whose the author?
Hugo,
Author is Brianna Parker