Company: Google (a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc.)
CEO: Sundar Pichai
Year founded: 1998
Headquarter: Mountain View, USA
Number of Employees (FY2023): 182,502
Public or Private: Public
Ticker Symbol: GOOGL(Class A) and GOOG(Class C)
Market Cap (Jun 2024): $2.16 Trillion
Annual Revenue (FY2023): $307.394 Billion
Profit |Net income (FY2023): $73.79 Billion
Products & Services: Android Auto | Android messages | Android OS | Calendar | Cardboard | Chrome | Chrome Web Store | Chromebook | Chromecast | Forms | GBoard | Gmail | Finance | Earth | Google Cast | Google Classroom | Google Cloud | Google Pay | Google Play Google Store | Google Street View | Google Wifi | Google for Education | Google + | Hangouts Waze | Wear OS by Google | Youtube
Competitors: Microsoft’s Bing| AOL | Baidu | Verizon | Yahoo | Ali Baba Group | Ask | Yandex | Apple(application & mobile) | Amazon(product search) | eBay | WebMD (health search) | Facebook | Twitter | Linkedin (job search) | Disney | Netflix (video services)
Fun Fact:
- There are more than 5.9 million Google searches per minute, translating to 8.5 billion daily searches.
- In 1997, Google almost sold its search engine for $1 million to Yahoo. Now, it is worth trillions of dollars owing to its impact on digital advertising.
- Stanford University still owns the patent to Google’s original search algorithm.
An Overview of Google
Google was founded in 1998 by Larry Page and Serge Brin in California, USA. The duo formed a massive technology company as a research project at Stanford University. Since then, the company evolved exponentially and has become a tech giant in the mainstream media.
Originally called Google, the company was restructured into an umbrella organization named Alphabet in 2015 to make people comfortable with new services and products.
Since October 24, 2015, Sundar Pichai has been the CEO of Google.
The global search engine has revolutionized the digital world. It has made life easier. All it takes to gather information now is a click of the mouse. Google has continued to demonstrate evolutionary strides with its game-changing operations.
While Alphabet is no stranger to in-house innovations, it has become a juggernaut on the internet through acquisitions. A robust merger and acquisition spree has allowed the company to expand beyond its original search engine roots. Cloud computing and autonomous vehicles are some of its latest bets, affirming its commitment to innovation and diversification.
Recently, it has integrated artificial intelligence features and tools to enhance its search tool and user experience on its various products and services.
Google’s Strengths
1. King of the online search
Google is the undisputed king of the online search engine department. Stat counter reports that Google has a market share of 91.37% of searches worldwide on all platforms (desktop, tablet and mobile).
2. Unbeatable
Till now, competitors have yet to come close to challenging its position and reaching its market shares in search engines. Next closest competitors of Google are Bing (with 10.24%), Yahoo (with 2.68%), Yandex (with 2.34%) and Baidu (with 0.72%) market share in desktop search engines worldwide.
3. Most valuable brand
Google is a globally recognized brand. According to Visual Capitalist, Google is “the world’s most valuable brand list,” ranked # 3 behind Apple and Microsoft. In 2024, Google’s brand value will be $333.4 Billion, per the Visual Capitalist list.
4. Search queries
This robust brand processes more than 5.9M search queries per minute on average, equivalent to about 8.5 billion daily searches. It is the biggest traffic generator and has a clear advantage over competitors like Bing, Yahoo, Yandex, and Baidu.
5. Expanding beyond search
The massive revenue of $307.394 Billion (2023) that Google has garnered through advertisement has ensured its growth.
- Advertising accounts for about 77% ($ 237B) of total revenues. Advertising revenue on search accounts for the most significant share at 56.9% at $175.03, with YouTube ads accounting for 10.3% at $31.51 billion, with Google Network ads accounting for 10.2% at $31.31 billion. Alphabet is diversifying its revenue base to other streams.
- Cloud computing is one area that is becoming an essential aspect of the business amid the digital revolution and growing demand for storage. The unit accounts for 10% of total revenue at $33.09 billion.
- Google subscription platforms, including apps, games, or other content that generate recurring fees, diversify Google’s footprint beyond digital advertising. The unit accounts for about 11% of total revenue, generating $34.69 billion last year.
- Google Other Bets: It includes a combination of multiple operating segments such as Access/Fiber, Calico, CapitalG, GV, Verily, Waymo, Wing, and X, among others. The unit accounts for about 0.5% of revenue at $1.53 billion.
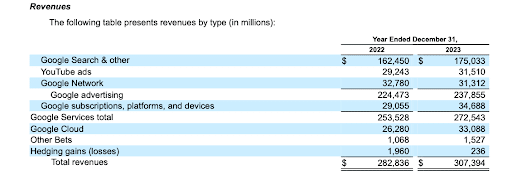
Image source: Google SEC filing
6. Adaptability
Google has successfully adapted mobile and Android technologies, giving it the potential to compete directly with Apple’s iPhone. The company controls about 70.79% of the market share of Android, compared to 28.46% of Apple’s iOS.
Google’s edge stems from getting its Android operating system onto as many devices as possible, from phones costing less than $50 to over $1,500. On the other hand, Apple only offers iOS on its devices, which come at a premium.
7. Rapid Growth
Google is one of the fastest-growing companies in the world. In 2001, the company had fewer than 300 employees; it increased 10-fold to 3000 in 2004, grew 10-fold again to 32,470 in 2011, and more than doubled to 61,814 by 2015. By 2018, Google had more than 98,000 employees and stood at about 182,502 as of the end of 2023.
Google’s Weaknesses
1. Privacy policies
Google has been slammed by many experts for its excessive reliance on privacy, especially when it comes to hiding information about algorithms. The company has since taken steps to address the allegations.
2. Overdependence on advertisement
Google’s overdependence on advertising has increased speculations regarding the company’s future. In 2023, the company made 77.8% of its total revenue from advertisement-related projects. Advertisement space is highly cyclical and competitive and relies heavily on macroeconomic conditions.
During deteriorating economic conditions, companies and brands slash their advertising budgets, hurting Google’s revenue base. Therefore, reliance on advertising is not sustainable, so the company must focus on other avenues, such as cloud computing and services.
Google needs to undertake a diversification strategy and aim to build a non-ad Business Model. In this effort, Google has introduced paid services such as Google Cloud, YouTube T.V. subscription, Google Play (sales of apps), and hardware (Nest, Pixel phones, Fitbit).
3. Boycott of Google and YouTube by major advertisers
Major brands boycotted against Google and YouTube when they discovered that their ads were running alongside extremist, hate-filled content. It has negatively affected Google’s image.
The companies that boycotted the search engine and video platform included Johnson & Johnson, AT&T, and Verizon in the U.S, L’Oreal, HSBC, RBS, the BBC, the Guardian newspaper, British retailer Marks & Spencer, Lloyd’s of London in the U.K., and Audi, Haves, Tesco, Volkswagen, Sainsbury. In addition to these brands, even the British government boycotted.
4. Unfair business practices
As the most used search engine, Google exploits this advantage unfairly to prevent the entry of new players in the sector. In the U.S., the company was recently sued for colluding with Apple to make it the default search engine for Apple’s browser.
It is reported that Google pays Apple an annual sum of $18 billion to maintain its status as the preset search engine on Apple devices, a practice that some consider to be anti-competitive.
5. Breach of privacy
Google has previously been caught red-handed over how it handles people’s data. In 2022, it was fined a record $391.5 million in one of the largest U.S. privacy settlements. The fine was handed after the company was found to have tracked users’ locations after they had opted out, affecting 2 billion users worldwide.
In Europe, Google was fined $56 million by France’s top court for breaching E.U.’s online privacy rules.
6. Failure in the social media revolution
Before social media giants like Facebook and Twitter emerged, most people relied on Google to access the latest news digitally. Now, people can access the latest news via social media platforms.
To protect its interests, Google attempted to launch several social media platforms unsuccessfully, like Google Plus and Shoelace, but these failed to gain traction and forced the company to shut down.
7. Poor pricing strategy
Google has raised the subscription price of its YouTube T.V. service from $49.99 per month as of 2020 to $72.99 monthly. While the increases reflect the rising cost of content, critics argue that the rise is absurd and continues working to the company’s disadvantage, given the stiff competition in the streaming business.
Most streaming services like Netflix, Disney+, and Peacock offer more content than the 80 T.V. channels provided by YouTube and charge between $5 and $15. Due to the price hike, Google could lose most of its 8 million YouTube T.V. subscribers.
8. Employees protest
Consumers dislike companies that advance evils and suppression in society or collaborate with the oppressors. In June 2020, more than 1,600 Google employees petitioned the company to stop offering its G-suite services to police departments in light of the Black Lives Matter protest.
9. Project Loon
In July 2020, Google experimented to offer the world’s first commercial high-speed internet. The service was introduced in Kenya, and Balloons provided affordable 4G internet to under-covered rural communities in East Africa.
However, the company “Loon” was shut down in 2021 because it failed to get low costs to build a long-term sustainable and profitable business.
Google’s Opportunities
1. Wearable market
The world’s market for wearable tech like smartwatches and fitness trackers was worth $120.54 billion in 2023. It’s expected to grow a lot, reaching $157.94 billion in 2024 and then going up to more than $1.4 trillion by 2032.
Google has already set sights on the massive market opportunity with the acquisition of Fitbit for $2.1 billion in 2019. With the acquisition, the company is already making smartwatches and fitness brands to better compete against Apple and Samsung in the lucrative and growing market.
2. Smartphones
The growing demand for smartphones and other mobile devices amid the digital revolution worldwide presents a tremendous opportunity for Google with its Android O.S. The market segment is growing at a 3.53% compound annual growth rate and is expected to be worth $0.5 trillion in 2024.
While about 6.94 billion smartphones are circulating worldwide, only Germany has a penetration rate of about 80%. Considering the 8 billion worldwide population, the reduced penetration level means there is a massive market for smartphones that Google can tap into with Android O.S.
The most substantial opportunity for Google is its noticeable efforts in providing Android operating systems. The operating system commands a global usage of 70.74% compared to 28.48% for iOS. This has strengthened its prospects of competing directly with Apple iOS.
3. Mobile application market
The global mobile application market is a dynamic and rapidly expanding sector. In the year 2023, the market’s value was recorded at $228.98 million. This figure represents the total revenue generated by mobile applications worldwide, encompassing a wide range of categories such as gaming, business, education, lifestyle, and entertainment apps.
Looking ahead from 2024 to 2030, the market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.3%.
While Google Play controls 23% of the market share in the segment, there is tremendous room for growth as more people use mobile devices and search for gaming, mobile health, fitness, and music and entertainment apps.
4. Cloud computing market
Based on findings from Grand View Research, the valuation of the cloud computing market stood at $483.98 billion in 2022. The market is projected to experience a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.1% over the period from 2023 to 2030. As businesses and enterprises explore ways of enhancing their digital activities, demand for cloud services continues to soar.
Amid the growing demand for computing resources and services, Google can tap into the cloud computing opportunities through its Google Cloud services.
It has also introduced a new digital store offering cloud-based software to all organizations. In line with this, the company collaborated with MobileIron, Inc., to integrate its cloud Orbitera commerce platform with MobileIron’s app distribution, security, and analytics capabilities.
5. Remote work
It is anticipated that the market for remote workspace services will expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23% from 2023 to 2032, reaching an estimated value of approximately $100 billion.
Google is already making moves to exploit the demand for remote work solutions. It has added video-calling features and other collaboration tools in Gmail to attract companies seeking to empower their employees to work from home or remotely as it looks to tap the multibillion-dollar opportunity.
6. Expand services to emerging markets
Emerging economies offer growth opportunities. Emerging economies allow the company to enhance its search engine market share and strengthen its digital advertising by targeting more people. In addition, the emerging markets would also offer an avenue for the company to sell its cloud services solutions and strengthen its revenue base.
7. Artificial Intelligence
Generative artificial intelligence transforms how products are produced and services are rendered in almost all sectors. Gen AI technology is expected to add between $2.6 trillion and $4.4 trillion in economic value across various use cases.
Google, a strategic player in the A.I. landscape, is well-positioned to harness the benefits of this technology. With its strong foothold in search, cloud computing, and advertising, Google has the potential to lead the way in A.I. innovation.
Google’s Threats
1. Decline in market shares
According to data gathered from marketers, Google’s U.S. digital ad revenue is expected to see a decline in market shares. Google’s digital ad revenue market share has declined, as shown:
- 2017: 38.8%
- 2018: 37.2%
- 2019: 36.2%
- 2020: 28.9%
- 2021: 28.6%
- 2022: 27.7%
- 2023: 26.4%
The decline is because of the growing competition from Facebook, Amazon, Instagram and Snapchat, which have become significant advertising players due to their massive user bases.
2. Gender bias
A Google memo published by its employer, James Damore, highlighting its diversity policy, has sparked an intense debate regarding the issue of gender bias and free speech in the company.
3. Alteration of information
Google has received considerable criticism over its alleged collaboration with China over a censored search engine project (Dragonfly).
4. Antitrust controversies
Google has been involved in antitrust controversies for years by both U.S. and E.U. lawmakers. The E.U. antitrust regulators imposed a 5 billion Euro fine, which Google sought to challenge.
5. Censorship policy
Google has not managed to protect itself from backlash over its censorship policy. Many whistleblowers have begun leaking information over its political and ideological leanings.
6. Aggressive competitors
Google faces significant competition from industry giants such as Facebook and Amazon. These rivals are gradually gaining ground, thanks to innovative features and growing user bases that could potentially shift market attention away from Google. Some of the competition that threatens Google’s long-term prospects includes:
- Competition on cloud computing from Amazon, Apple and Microsoft
- Competition on search as A.I. and Microsoft pile pressure with new engaging search features
- Competition in digital advertising from Facebook, Snap and Instagram
Likewise, Microsoft is investing billions of dollars into technology to refine its Bing search engine to be better equipped to take on Google.
7. Search businesses under threat due to Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence is slowly becoming a significant threat to the internet giant. The company’s search business is more threatened than ever as technology transforms how people ask and get answers online.
The emergence of A.I. Chatbots like OpenAI’s ChatGPT Anthropic’s Claude pose significant dangers to the usual search business. While Google Search was the most preferred option for asking and getting answers, people increasingly use chatbots, given the enhanced user experience. While chatbots are not perfect
Replacement for Google searches will surely eat into its market share.
Image source: Statista
8. Anti-encryption drive to reduce child abuse
In the past few years, cases of online child exploitation images have increased from thousands per year to tens of millions. Multiple governments and child welfare groups are pushing for the elimination of encryption technologies to ensure child exploiters online are revealed promptly.
Even though Google has pledged to standardize disclosure of the culprits, governments and child welfare groups insist that Google and other tech giants stop using encryption technologies. With user anonymity online, Google can retain customers.
9. Tensions with China
Google had planned to provide cloud service in China but was forced to scrap the plan due to rising geopolitical tensions. If political tensions spread to other regions worldwide, it could affect Google’s operations.
10. Email Scams
Growing cases of email scams propagated through Gmail pose one of the biggest dangers to Google’s reputation in the industry. Phishing, whereby individuals and companies are increasingly targeted, has become rampant, leading to the loss of confidential information or intellectual property to breach customer data.
Most email scams involve attackers imitating well-known companies or brands to exploit the trust and familiarity of users with specific brands. Microsoft is one of the most abused brands, closely followed by Adobe, DHL, and Google.
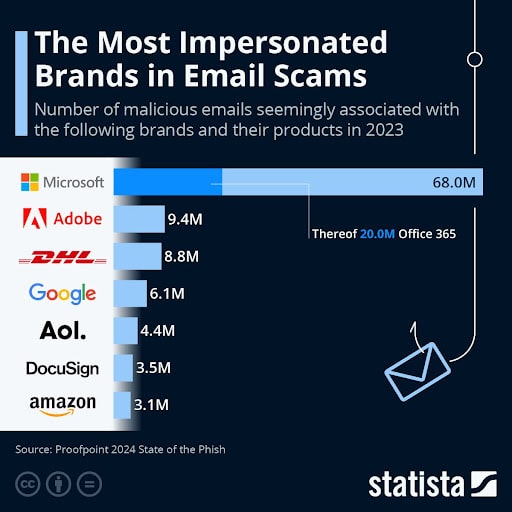
Image source: Statista
Conclusion
The SWOT analysis of Google shows the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of the biggest online search engine. The popularity of Google allows it to enjoy huge profits.
The search engine keeps growing every year, and its technology is improving. If Google addresses its weaknesses and threats, no competitor can outperform or match this company.
References
- Neufeld, D. (2024 January 29). The Top 100 Most Valuable Brands in 2024. VISUAL CAPITALIST.
- Jones, P. (2024 January 11). 34 Eye-Opening Google Search Statistics for 2024. Semrush Blog.
- Schrieberg, D. (2017 March 23). U.S., U.K. Boycott Of Google And YouTube By Major Advertisers Spreading Over Hate Content. Forbes.
- Pierce, D. ( 2023 October 23). Google reportedly pays $18 billion a year to be Apple’s default search engine. The Verge.
- Ball, S. (2023 January 10). Meta and Google fined. Who’s next in the data scandal saga?. ERP TODAY.
- Rosemain, M. (2020 June 19). Top French court upholds $56 million Google privacy breach fine. Reuters.
- Heater, B. (2020 April 29). Google is shutting down Shoelace, the social app you’ve probably never heard of. Tech Crunch.
- Dave, P. (2020 June 23). Google faces employee petition to end tech sales to police. Reuters.
- Miriri, D. (2020 July 8). Alphabet’s Loon launches balloon internet service in Kenya. Reuters.
- Amuge, O. (2023 June 5). How $483.98bn cloud computing can boost financial performance of Nigerian FinTech firms. Business a.m.
- Chui, M. (2023 June 14). The economic potential of generative AI: The next productivity frontier. Mckinsey.
- Ceurvels, M. (2018 March 19). Data Suggests Surprising Shift: Duopoly Not All-Powerful. EMARKETER.
- Warren T. (2018 July 18). Google fined a record $5 billion by the EU for Android antitrust violations. The Verge.
- Gallagher, R. (2020 July 8). Google Scrapped Cloud Initiative in China, Other Markets. Bloomberg.
- Paul, K. (2020 June 11). Battling anti-encryption drive, tech companies pledge new child abuse disclosures. Reuters.
- Statt, N. (2018 October 11). Leaked Google research shows company grappling with censorship and free speech. The Verge.
- Gartenberg, C. (2018 October 5). White House calls on Google to abandon controversial Chinese search engine project. The Verge.
- Meyersohn, N. (2017 August 9). The Google controversy in two minutes. CNN.
Tell us what you think? Did you find this article interesting?
Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below.












This article helps me to know about google shortly.
Thanks
perfect for my ETLV
Thanks Mouloud, happy reading 🙂