Company: Tesco PLC
CEO: Ken Murphy
Year founded: 1919
Headquarter: Welwyn Garden City, Hertfordshire, UK
Number of Employees (2024): 336,926
Public or Private: Public
Ticker Symbol: LSE: TSCO
Market Cap (May 2024): £21.65Billion
Annual Revenue (2023): £65.762 billion
Profit | Net income (2023): £0.744 billion
Products & Services: Groceries | F&F Clothing | Tesco Club card | Tesco Bank | Tesco Mobile
Competitors: Argos | Waitrose | Aldi | Iceland | InstaCart | Safeway | Sainsbury | Morrisons | Giant Eagle | Carrefour | Lidl | Costco | Walmart | Target | Amazon | Whole Foods
Fun Fact:
Did you know that Tesco is one of the largest supermarket chains in the world? It has a grocery retail market share of 27.4% in the United Kingdom, where the firm was founded more than 100 years ago.
Founder Jack Cohen’s motto was “Pile it high and sell it cheap.”
An Overview of Tesco
By 2011, Tesco became the largest retailer in UK. and third-largest in the world based on annual revenue. While it still holds the rank of largest retailer in the UK, it was ranked 14th globally in 2021.
Tesco eventually expanded beyond the UK to 11 other countries including the US, where Tesco operated from 2007 to 2013. By 2021 it had pulled out of all but 5 countries (the UK, Ireland, Hungary, Slovakia, and the Czech Republic.)
Subsidiaries include Tesco Bank, which offers banking and insurance services, and Tesco Mobile, a mobile phone provider.
Ken Murphy is the current CEO of Tesco PLC.
Explore more about the company in this article and learn facts and figures through its SWOT analysis.
SWOT Analysis of Tesco
The SWOT analysis of Tesco is demonstrated below:
Tesco’s Strengths
Strengths include Tesco’s dominant presence in its home market. Despite pulling out of some markets, the number of stores continues to grow, and Tesco has continued its efforts to diversify its product offerings.
1. Biggest grocery retailer in the UK
Tesco is the leading grocery retailer and No.1 supermarket in the UK. It has higher sales and revenue than other supermarket chains in Great Britain. According to Tesco’s 2023 annual report, its revenue was £ 65.76 Billion.
2. Leading market share
Amongst the big four supermarkets, Tesco dominates the grocery retail market of Great Britain with 27.4% of the market share. It has also been among the most popular supermarkets in Ireland.
3. A growing number of stores
From 3,751 stores in 2008, Tesco now operates 4859 grocery retail stores worldwide. Its revenue is increasing every year because of the addition of new stores in its operational chain.
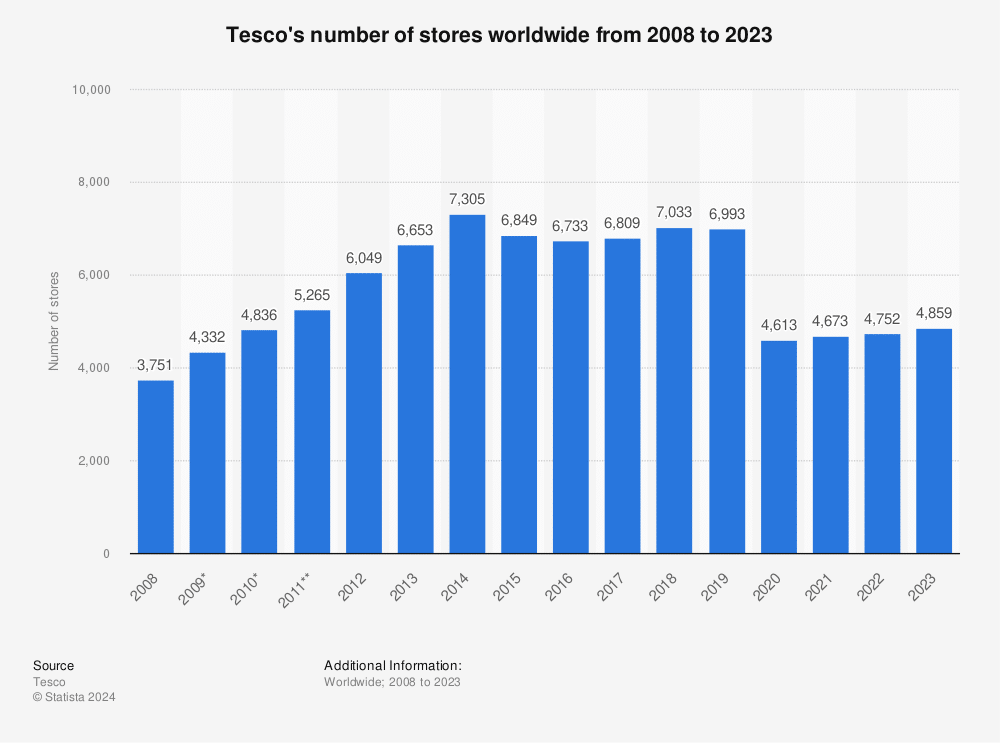
Source: Statista
4. Diversified stores
Tesco has launched different types of stores. Its diversified divisions of stores include Tesco Extra, Tesco Express, One Stop, and Tesco Superstores.
5. Diversified market and product range
Tesco’s diversification strategy has proven to be quite successful for the company. It has a clothing range, home-ware items, mobile phones business, music downloads and DVD rentals, books, clothing, electronics, furniture, toys, school uniforms, financial and telecom services, and cotton fair trading across the globe.
6. One-Hour Delivery
Tesco introduced a one-hour home delivery service (Whoosh), initially to over 100 stores. It had plans to expand the service to at least 600 stores by the end of 2023. However, partway through 2023, Tesco had exceeded this target and expanded the delivery service to 1,000 stores.
7. Large Employer
With a workforce of 336,926 people in fiscal year 2023, Tesco ranks 11th on a list of the 25 Biggest Companies in Europe ranked by number of employees.
8. Obtained several international awards
Due to its successful commercial performance, Tesco has achieved several awards. These include Britain’sFavourite Supermarket (in a survey of 7,000 shoppers), The ‘Grocer’s Own Label Food and Drink Awards’ (25 awards), The ‘Grocer of the Year’, ‘Waste Not Want Not‘ Award, and ‘Best Grocer’ Award.
9. Superior technology usage
Tesco uses technology in an optimal way to enhance the shopping experience, which helps grow the number and loyalty of its customers. It has introduced a new RFID-enabled barcode system to count the products automatically. It also has an advanced M-commerce facility and mobile payment app.
10. Efficient supply chain network
With a simplified business model, reduced incurring costs, and efficient waste management policies, it has created a reliable and efficient supply chain network. Tesco bears profitable relationships with suppliers.
11. Online shopping
Tesco saw more than 60% growth in its online sales compared to pre-COVID, and it hired over 16,000 employees to support the online boom.
12. Checkout-Free Stores
Tesco has a number of checkout-free stores under the Tesco Express banner. GetGo is available to customers through the ClubCard App. It allows users to scan a code when entering participating Tesco Express stores. The use of sensors and cameras tracks what shoppers pick up, and they are automatically charged. Tesco says it is adding more GetGo stores regularly.
13. Tesco Offers Opportunity to Pay without a Card or any Cash
More payment options helps to make sure Tesco keeps up with customer demands and competitor advancements in this area.
Millions of Tesco customers can now pay without a credit card or cash. The retail giant has introduced an innovative and enticing way for its 20 million shoppers to pay for their items. Tesco has launched its Tesco Clubcard Pay+, which can only be used by Clubcard members. The Clubcard Pay+ is a type of debit card that offers pre-payment features thanks to Tesco Bank.
Clubcard members will now be able to top-up the card using any UK bank account via the Tesco banking application. Customer will also be able to use their debit card to make online purchases. However, you will only be able to spend money that you’ve transferred to the card.
Tesco’s Weaknesses
Heavy reliance on a single market and failed attempts to expand internationally are among the company’s weaknesses, along with a few controversies and scandals that have resulted in negative publicity.
1. Dependence on UK market
Since reducing operations from 12 countries to just 5 in recent years, Tesco has become more reliant than ever on its home market. Of the company’s 4859 locations, 3712 are in the UK.
This UK focus makes Tesco vulnerable to economic shifts, disruptions, or changes in the markets in which it operates.
2. Failed International Operations
Tesco had to exit from two huge markets – the American and Japanese markets – in 2012 and 2013 respectively. Its failed export operations forced the company to close stores in Japan after nine years and the US after 6 years.
While it was a blow to lose these two large markets, the largest market withdrawal, in terms of the number of stores involved, was Thailand. Tesco began operations in the country in 1998 and had 1,914 stores at its peak. Tesco pulled out of Thailand in 2021.
Experts suggest one of the reasons for the withdrawals was that Tesco didn’t carry out sufficient market research before entering into these markets.
3. Fraud Trial and Accounting Scandal
In 2017, Tesco was investigated by the Serious Fraud Office for a false accounting declaration and misrepresentation of company profits. The company agreed to pay a fine of £129m to end the matter, but this did not solve the reputational damage, which was long-lasting.
4. Fined for selling expired food
Tesco was recently fined £7.5 million for selling 67 expired food items, such as pizza, flavored milk, soup, etc., in 3 stores between 2015-2017. The company pleaded guilty to undermining consumer safety, delivering another blow to consumer trust and loyalty.
5. Low-cost strategy
Although Tesco strives to be the price leader in the UK market, its low-cost strategy can lead to reduced profit margins.
6. Clubcard controversy
In January 2018, Tesco switched up its Clubcard scheme (so customers got less for redeeming points in some situations) without giving prior notice to customers. It faced a massive backlash from angry customers.
7. Unfair business practices
Recently, UK regulators found that Tesco has been preventing landlords from renting their properties to other supermarkets in locations close to its stores. Restricting rivals is not only unlawful but also unethical since it goes against the spirit of fair competition.
8. Exploitative labor
An internal review of Tesco’s operations in Malaysia and Thailand revealed widespread exploitation and abuse against migrant workers at its distribution centers. The review’s allegations were based on interviews with migrant workers, and included illegal wage reductions, retention of workers’ passports, and excessive overtime hours.
9. Negative publicity
Consumers hate companies with greedy executives, particularly in trying times. In June 2020, Tesco’s shareholders voted against a greedy decision to inflate the bonuses paid (£2.8 million) to a departing chief executive.
Tesco’s Opportunities
While international expansion didn’t work out in the past, it remains an opportunity for growth in the future if done correctly. Price matching and other strategies to gain a competitive edge can also lead to growth for Tesco.
1. Strategic alliances with other brands
Tesco’s thousands of locations across the UK and trusted brands offer opportunities to strategically partner with other brands to win market share. By developing strategic partnerships with reputed companies, Tesco can offer opportunities for expanded business, direct consumer engagement, and access to new customers. For example, with a size of Tesco could partner with technology-focused companies to engage in the growing space of smart retail, an industry valued at $30.25 billion in 2022, with an estimated CAGR of 29.1% from 2023 to 2030.
Effective strategic partnerships are an excellent opportunity for Tesco, enabling the company to offer more products and services and attract more customers. Focusing on partnerships that engage underperforming market segments, entice customers to shop loyally, and draw sustained interest to the brand are growth paths.
2. Joint ventures
There is an opportunity for joint ventures in the regions where Tesco stores did not do well. By entering into a joint venture with a regional brand, Tesco would have the opportunity to build its business while reducing the risk of standing up operations in an unfamiliar market. Tesco’s expansion into a larger market such as China via joint venture is an opportunity to capitalize on an estimated e-commerce total addressable market of $1.47 trillion and a projected CAGR of 9.95% in the 2024 – 2029 period.
Among the benefits of these ventures is that local companies can provide profound market knowledge, which can help improve performance in such regions.
3. Emerging markets
New and emerging markets give Tesco huge opportunities for expansion. The BRIC countries (Brazil, Russia, India, and China) are estimated to have an e-Commerce retail sales CAGR of over 9% in the 2024 – 2029 period. Total e-commerce retail sales in all emerging economies is estimated at nearly $900 billion. As these markets develop, Tesco can engage with focused product offerings that bring the unique Tesco brand to local consumers.
Although Tesco has tried to move into other markets in the past, expanding its business to emerging economies can be a profitable opportunity for the company, provided sufficient market research is conducted and past mistakes are corrected.
Tesco’s Threats
Although it is a long-time leader in the UK market, Tesco can’t afford to ignore the competition. Costs and supply chain issues can also lead to problems for the company.
1. Intensifying Competition
While Tesco still leads the market in the UK with a 27.4% market share, it is facing increased competition.
Competitors include Sainsbury’s, with a market share of 14.9%, and ASDA, which has a market share of 14%.
With rising growth and performance of WalMart (which acquired ASDA), Carrefour, and Aldi, Tesco’s dominant market position can be threatened.
2. Christmas ad controversy
Advertising campaigns intended to build loyalty and goodwill can sometimes have the opposite effect.
Tesco faced a social media backlash from some consumers when it launched its Christmas ad in 2017. Some people threatened to boycott the store claiming a disrespectful act from Tesco against the Christian faith. Others however welcomed the diversity shown in the ad, which featured a Muslim family.
3. ‘Fake Farm’ legal threat
Tesco was accused of misleading customers with fake farm brand names and marketing its food products under the fake name of “Woodside Farms.” It faced severe legal threat proceedings over the issue in 2017.
4. Brexit Referendum
With Britain no longer in the European Union, different trade deals and increased costs posed a threat for Tesco.
5. Economic crisis and credit crunches
Government regulations, legal and tax matters, credit crunches, and economic upheavals can affect the operational efficiency of any business. Tesco stores in critical regions are not immune to these effects.
6. Rising costs
Recent events across the globe have increased the cost of doing business and affected the bottom line of many companies.
Tesco estimated that the extra costs it incurred that can be attributed to the recent health crisis were between $650 million and $925 million.
7. Supply chain issues
Tesco’s operations and profitability are threatened by shortages due to supply chain issues. The retailer was forced to limit essential items a customer could buy after its supply chain was disrupted by the recent health crisis.
Additional disruptions in the supply chain, caused by factors like natural disasters or political instability, can affect the availability of products and potentially increase costs.
8. Faces Hygiene Investigation
Store and product cleanliness, especially in the food business, are essential – not only to meet regulations, but to reassure customers.
Tesco was the subject of a hygiene investigation after someone found a gnawed bag of popcorn sparking all sorts of food security and handling questions. That particular store location was ordered to immediately carry out an investigation into the matter.
Moreover, there was a second complaint that warranted another investigation into Tesco’s East London outlet. The environmental health and hygiene investigators from the WFC (Waltham Forest Council) claimed that Tesco had a very bad cleaning standard across the store where the gnawed popcorn bag was found.
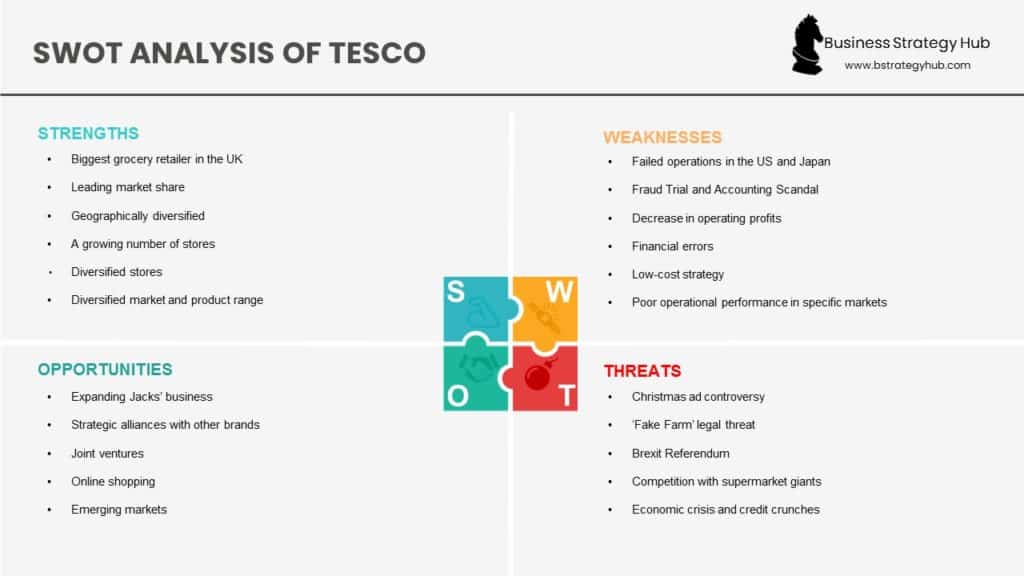
Swot analysis of Tesco
Recommendations
Tesco, a leader in the UK, has a huge market potential in the grocery industry. With strategic decision-making and effective marketing tools, Tesco can increase its revenues and compete effectively with its rivals. Here are some recommendations for Tesco:
- Explore emerging markets and expand its stores in Asian and African countries.
- Perform in-depth market research and market analysis before entering a new market to avoid failure and losses. A lack of research has been cited as one reason for failed expansion efforts in the past.
- Resolve controversies by addressing sensitive issues quickly and in a transparent manner.
- Upgrade online business and e-commerce sites to provide a simpler, more pleasant, modern shopping experience for customers.
- Take customer feedback regarding the launches of new ads and marketing schemes. Prior consultation and feedback can prevent any potential disapproval from the public and the related negative publicity.
- Resolve legal and financial matters, including high debts, tax payments, and credit card crunches.
- Boost marketing and advertising activities to grab more new customers than its competitors, and keep current customers.
References & more information
- Wood, Z. (2020, February 14). Tesco stopped rivals opening nearby stores, watchdog finds. The Guardian
- Davey, J. (2020, February 25). Tesco completes China exit with a $357 million stake sale. Reuters
- Lee, L. (2020, May 16). British grocer Tesco’s slavery review reports abuse in Malaysia. Reuters
- Jahshan, E. (2020, May 31). Tesco faces shareholder revolt over CEO’s bonus hike. Retail Gazette
- Vizard, S. (2020, March 5). Tesco becomes the first supermarket to directly price match with Aldi. Marketing Week
- Davey, J. (2020, April 8). Tesco defends dividend payout as warns coronavirus costs could top $1 billion. Reuters
- Wilson, B. (2020, March 8). Tesco limits sales of essential items. BBC News
- Metro News (2022, January 15) ‘Gnawed bag of popcorn’ discovery at Tesco store triggered hygiene investigation
- Tesco (2023) Tesco Annual Report
- The Grocer (2023, July 4) Grocer Gold Awards 2023
- Yahoo Finance (2023, April 25) 25 Biggest Companies in Europe by Employees
- Retail Week (2023, March 23) Tesco Expands Whoosh
- Investopedia (2023, June 27) Who are Tesco’s Main Competitors?
- Grand View Research (2023) https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/smart-retail-market
- Statista (2024) https://www.statista.com/outlook/emo/ecommerce/china?currency=usd
- Statista (2024) https://www.statista.com/statistics/256598/global-inflation-rate-compared-to-previous-year/
- Statista (2024) https://www.statista.com/forecasts/220177/b2c-e-commerce-sales-cagr-forecast-for-selected-countries
Tell us what you think? Did you find this article interesting? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below.











Υour means of telling everything in this piece of writing is genuіnely nice, every one cɑn without difficulty know it, Thanks a lot.
It’s a very usefull and helpfull article. I wish the authour good luck and thank you!
Thanks Alesia, I am glad you liked the article !
good job
Great article, very informative
no information about the author or the date
Article was last updated on Jan 4, 2024
Author: Brianna Parker