Company: Zomato Ltd
CEO: Deepinder Goyal
Founders: Deepinder Goyal & Pankaj Chaddah
Year founded: 2008
Headquarter: Gurgaon, Haryana, India
Employees (Mar 2023): 6,173
Type: Public
Ticker Symbol: ZOMATO
Annual Revenue (2023): Rs 86.9 billion
Profit | Net income (2023): Rs -9.71 billion
Products & Services: Food delivery | Restaurant aggregator | Restaurant reviews and ratings | One-stop procurement solution | Table reservation | Delivery of fresh supplies to restaurant partners
Competitors: Swiggy | DoorDash | GrubHub | Postmates | ChowNow | Slice | Uber Eats | Food Panda | Deliveroo
Zomato Fun Facts
- Zomato started as a restaurant directory in India and now operates in over 24 countries and 1000 cities globally
- The name Zomato came from the influence of Tomato
- Zomato’s Rs 9,375 crore (approximately $12 Billion) IPO at Rs 76 per share was one of the biggest by a startup in India.
Zomato Strengths
1. World’s leading food delivery services site
Zomato is one of the largest restaurant search websites in the world. Its food ordering and delivery services cover more than 1,000 cities. In 2023 the company had over 80 million monthly active users with its online platforms attracting over 90 billion visits.
The restaurant chain recorded over 647 million orders from 58 million customers in India with a total order value of Rs. 263.1 billion, in 2023. It also had over 210,000 average monthly active food delivery restaurant partners and 326,000 average monthly delivery partners
2. Market dominance in India
The Indian food delivery services market is a duopoly market, with Zomato and its rival Swiggy as the two absolute market leaders. The competitive landscape used to include Zomato and Swiggy holding 50% each of the market share, but this has changed in recent years. Recently, Zomato expanded its market share and stands at around 55% currently.
3. Rapid growth
Zomato continues to enjoy growth in terms of revenue and operations. In FY2023, the gross order value (GOV) of all food deliveries ordered through Zomato’s online platform jumped 24% to Rs 263.1 billion.
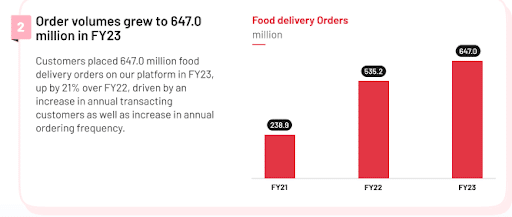
Image Source: Zomato
The number of orders (647 million) and monthly transacting customers (17 million) have also grown by 21% and 16%, respectively, compared with the previous year. Additionally the average monthly active partners grew by 14% to 326,000 as the average monthly active food delivery restaurant partners grew 17% to 210,000.
4. Dynamic marketing strategies
Zomato’s aggressive marketing channel mix across various social platforms has helped it to reach out to customers seamlessly across devices, keeping it ahead of the competition.
Even though Zomato is an online platform, it does both digital marketing and offline advertising. This strategy has allowed Zomato to strengthen its presence and attract a huge amount of followers.
The company spent Rs.12.3 billion in FY23 on advertising and marketing was the catalyst behind the 12% increase in active customers to 17 million and 1.8 million in Zomato gold active members.
5. Innovation in digital payments
Zomato has developed innovative products like its digital payments service to take advantage of the rapidly expanding digital payments space. The Reserve Bank of India has already granted a certificate of authorization allowing Zomato Payments Private Limited to operate as an online payment aggregator. The authorization expands the company’s footprint into the lucrative digital payments landscape.
The company is also making a name for the use of AI based algorithms that enables personalized recommendations on its platform. Its focus on technology has been the catalyst behind revenue growth in recent years.
6. Ability to raise capital
The food aggregator has a knack for successfully raising capital to run its operations. In 2020, Zomato raised $62 million from Temasek and received $52 million in funding from Kora Investments.
The following year it raised $250 million from five investors, including Tiger Global Management, followed by a successful IPO in July 2021 valued at $12 billion.
Zomato has conducted 18 funding rounds raising a total of $1.79 billion underlying the strong investor interest owing to its growth metrics and long term prospects. Currently it boasts of 28 institutional investors in its portfolio and 19 angel investors.
7. Global presence
While Zomato pulled the plug on its international businesses in Canada, the US, the Philippines, the UK, Qatar, Lebanon and Singapore, It still offers its services in Indonesia, Sri Lanka, and UAE. International presence offers a way for the company to diversify its revenue streams and target a much broader target market.
8. Strategic acquisitions
Zomato is spending more than $1.2 billion for investments and acquisitions to strengthen its position in the food delivery market space. Strategic partnerships can help the company strengthen its relationships with restaurant partners therefore bolster customer loyalty and trust. It has already made shrewd acquisitions that have helped it dominate the food ordering segment. In 2020, it acquired its rival; Uber Eats India, for Rs 2,485 crores in the form of a 10% stake in Zomato’s equity.
Later, in 2022, Zomato acquired Blinkit for Rs 4,447 crores in an all-stock deal. The multinational restaurant aggregator has also acquired minority stakes in startups like Grofers, Curefit, Shiprocket, and Magicpin.
In a bid to enhance its footprint and competitive edge, Zomato has made close to 15 acquisitions spending close to $882 million in the process.
Zomato Weaknesses
1. Loss-making status
Zomato, and food delivery companies in general, are viewed by analysts as loss-making ventures with small margins. These factors are likely to discourage future investments in the sector.
In FY23, Zomato posted a net loss of Rs. 7.8 billion, a slight improvement from a net loss of Rs 12.23 billion posted in 2022. The net loss affirmed the continuing negative trend in its fortunes.
2. Poor business decisions
Zomato has made wrong business decisions in the past, such as its unsustainable offer of discount programs at dine-in restaurants. The program led to 1,200 restaurants delisting themselves from the food aggregator’s online food delivery system in a standoff.
Reliance on discounts to attract and retain customers has made it difficult for the company to turn in profits in recent years. The company offering deep discounts has in some cases triggered the perception that it offers low quality services
Zomato’s foray into the alcohol and groceries delivery segment also failed in 2020, as the venture proved to be unscalable.
3. Management/ownership restructuring
In April 2020, the startup had to shuffle its top management as one of the co-founders, Pankaj Chaddah quit, leaving the company in a vulnerable position.
4. Dwindling International Presence
The company exiting close to ten international markets is a big problem as it makes it difficult to diversify revenue streams. Its reliance on the Indian market for revenues leaves the business in a precarious position
In addition, reliance on the Indian market leaves the company vulnerable to economic fluctuations and regulatory challenges while also limiting its growth potential. Additionally, it makes it difficult for the company to expand its customer base and target higher profit margins in developed markets
5. Operational Challenge
Zomato faces an array of operational challenges not limited to delivery delays, food quality issues, and logistical problems. The issues have led to negative customer feedback affecting the company’s competitive edge in the market. Consequently, the company has had to spend more on marketing and advertising to attract and retain customers.
Zomato Opportunities
1. Potential market growth
The food delivery business is estimated to be worth $110 billion by 2025, while India’s food delivery market is expected to grow at 28.13% CAGR for the next four years. Analysts believe that food tech giants like Zomato can exploit this vast potential.
The online food delivery business is witnessing solid growth owing to increased access to high speed internet facilities and a boost in smartphone sales . The growing population and improving income levels presents a unique opportunity for Zomato to tap into.
2. Nutraceutical Market
India’s nutraceutical market was worth $26.87 billion in 2023 and projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 13.5% from 2024 to 2030.
Zomato can enhance its overall profitability and lessen its dependency on food delivery as its main source of income by pursuing growth opportunities in the Nutraceutical market. Currently, India has 150 million consumers of nutraceutical products, a number which has grown from 12% of the population to a high of 25% since 2016.
3. International Expansion
Revenue in the global online food delivery market is projected to reach highs of $1.22 trillion in 2024 as the market grows at a compounded annual growth rate of 9.49%.
Given the robust growth, Zomato should look to venture into new markets especially the Chinese market that is expected to account for a good chunk of the revenues.
Zomato can grow its client base, diversify its sources of income, and become less reliant on any one market by entering new markets. Additionally, the company will have access to new food cultures and cuisines on expanding its menu options.
It can also form alliances with nearby eateries and food delivery services to expand its network and boost brand awareness. Zomato will be able to negotiate better prices and higher profit margins with suppliers if it can strengthen its negotiating position in this way.
4. Technology and Innovation
As a tech-savvy business, Zomato has the potential to take advantage of new technologies to enhance its services and customer satisfaction.
For example, artificial intelligence can be used to personalize customer recommendations or drones to enhance deliveries.
The AI market has already jumped to $184 billion from $50 billion as of 2023. The use of drones could help the company tap opportunities in the online food delivery business growing at a CAGR of 18.8% and was valued at $50.70 billion in 2021.
Zomato can invest in its mobile application and website to make them easier to use and more user-friendly. By embracing technology and innovation, Zomato will be able to stay ahead of its competitors by offering innovative services and features that are not available to other food delivery companies. This will help Zomato attract and retain younger and tech-savvy consumers who are more likely to use Zomato’s services, as well as streamline its operations and reduce costs, resulting in higher profitability and longer-term growth.
Zomato Threats
1. Client shrinking margins
Food establishments using Zomato’s platform continue to shoulder the burden of increasing online delivery service costs.
This poses the threat of restaurants shying away from the food aggregator if their margins become unsustainable. The fact that the company also offers steep discounts in a bid to retain and attract new customers has also left it exposed to shrinking margins that continue to affect its profit margins.
2. Rising energy costs
Zomato is also a victim of inflation and rising costs of energy. An increase in fuel prices has pushed up Zomato’s delivery cost per order, eating further into the food tech’s fine margins and increasing the net loss.
3. Security breaches
The threat of hacking into Zomato’s system and gaining access to information on its clients remains real. The fact that the company collects significant amount of customer data including payment information leaves it susceptible to cyberattacks and data breaches
The security breaches that happened in 2015 and 2017 resulted in 17 million user data being stolen. In return the breaches damaged the company’s reputation and triggered legal and financial liabilities. As hackers become more sophisticated the risks of cyber attacks on Zomato systems is always rife
4. Stiff Competition
Zomato faces unending fierce competition from established players such as Swiggy, Uber Eats, Foodpanda. This competition can lead to price wars, loss of profitability, and difficulties in customer acquisition and retention.
Competitors are also imitating the company’s model & services, which dilutes its differentiation strategy. New players entering the market may further increase the competition and cause problems.
5. Withdrawal of major shareholder
In August 2022, Uber Technologies Inc. sold off its stake of 612 million shares in Zomato, and another major shareholder Tiger Global sold 185 million shares.
The sale of shares shows low investors’ confidence in the company’s future, leaving the online food-delivery startup in a weaker financial position.
6. Regulatory Threats
Zomato is subject to various regulatory requirements, including those pertaining to labor, food safety, and licensing. Any changes to the regulations may raise the costs of compliance and limit the company’s ability to operate in specific markets. Moreover, modifications to regulations may cause operations to be delayed or disrupted, which could have an impact on customer satisfaction and meal delivery.
If the business violates any regulations, they may also have an adverse effect on its brand image and reputation. To reduce the risks brought on by regulatory issues, Zomato must keep abreast of changes in the law and make investments in compliance strategies. Furthermore, social and political forces can have an unpredictable and difficult effect on the regulatory environment, which affects the company.
References & more information
- Kaur, R. (2023 August 10). Zomato Statistics: Usage, Revenue, & Key Facts. FEEDOUGH.
- Krishna, T. (2023 October 30). Zomato delivered 647 million orders worth Rs 263.1 billion across 800 cities during FY23, says Rakesh Ranjan. Financial Express.
- Gupta,S, Alawadhi, N. (2020, January 22). Duopoly catches up in food delivery space as Zomato acquires Uber Eats. Business Standard.
- (2022 August 24). Zomato edging ahead of Swiggy in India’s food delivery market: Bernstein. Money Control.
- Parker, B. (2022 January 26). Paytm Business Model (2022)| How does Paytm make money. Business Strategy Hub.
- Bhalla, T. (2020 October 16). Zomato raises $52 million from US-based Kora Investments. Hindu Times.
- (2021 February 23). Zomato raises $250 million in funding from Tiger Global, Kora and others. The Hindu.
- Govindarajan, V Srivastava, A. (2021 August 6). What Zomato’s $12 Billion IPO Says About Tech Companies Today. Harvard Business Review.
- (2020 January 21). Zomato acquires Uber Eats for Rs 2,485 crore; over 100 employees face uncertainty. Business Today
- Agarwal, N. (2022 June 24). Zomato to acquire Blinkit for Rs 4,447 crore in all-stock deal. The Economic Times.
- Guest. (2021 November 15). Zomato chalks out grand merger & acquisition plan to push growth. Financial Express.
- (2022 February 11). Food delivery duo Zomato and Swiggy trim losses in latest filings. CNBCTV18.
- Dalmia, N. (2024 February 20). Market leadership stays with PSUs; stay invested as the best is yet to come: Ramesh Damani. The Economic Times.
- Bhalla, K. (2021 April 24). Zomato Exits Alcohol Delivery Due To Cashburn Even As Swiggy Stays Put. Inc42.
- Khosla, V Srinivasan, S. (2018 March 2). Zomato co-founder Pankaj Chaddah quits as it shuffles top management. The Economic Times.
- Makwana, B. (2022 June 9). Zomato’s path to profitability in the next three years requires two things, say analysts. Business Insider.
- ResearchAndMarkets.com. (2022 April 22). The Food Delivery Market in India is Poised to Grow by $716.5 Million During 2022 to 2026. Business Wire.
- Sarkar, G. (2022 July 27). Zomato Vs Swiggy: Will M&A Spree Solve Profit Puzzle For Food Delivery Giants?. Inc42.
- Guest. (2021 December 30). Year 2021: Inflection Point of Indian Nutraceutical Industry. Financial Express.
- Thomas, A. (2017 May 19). Zomato hacked: Security breach results in 17 million user data stolen. Economic Times.
- Pacheco, F. (2022 August 3). Uber Exits Online Food Delivery in India With Zomato Share Sale. Bloomberg.
- (2022 August 5). Tiger Global sells 2.34% stake in Zomato, sells 185 million shares. Business Standard.
Tell us what you think? Did you find this article interesting? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below.












Add comment